Imagine a single Wi-Fi network seamlessly connecting thousands of devices across a smart city, industrial complex, or an agricultural field while consuming minimal power.
In a world where IoT (Internet of Things) applications rapidly expand, reliable, long-range, and power-efficient connectivity is more crucial than ever. Although ubiquitous and fast, earlier Wi-Fi versions were not designed for these large-scale, low-power needs. Wi-Fi HaLow (IEEE 802.11ah standard) steps in as a game-changer. In this article, we’ll explore how Wi-Fi HaLow works, its advantages, and why it’s the future of IoT connectivity.
What is Wi-Fi HaLow?
Wi-Fi HaLow, based on the IEEE 802.11ah standard, is a wireless networking protocol designed to provide extended-range Wi-Fi connectivity with lower power consumption, making it particularly suitable for Internet of Things (IoT) applications.
Key Characteristics of Wi-Fi HaLow
Wi-Fi Halow is an ideal connectivity standard that addresses the unique connectivity challenges of IoT, like long-range coverage, low power consumption, and high device capacity over a large area. The characteristics of Wi-Fi HaLow include:
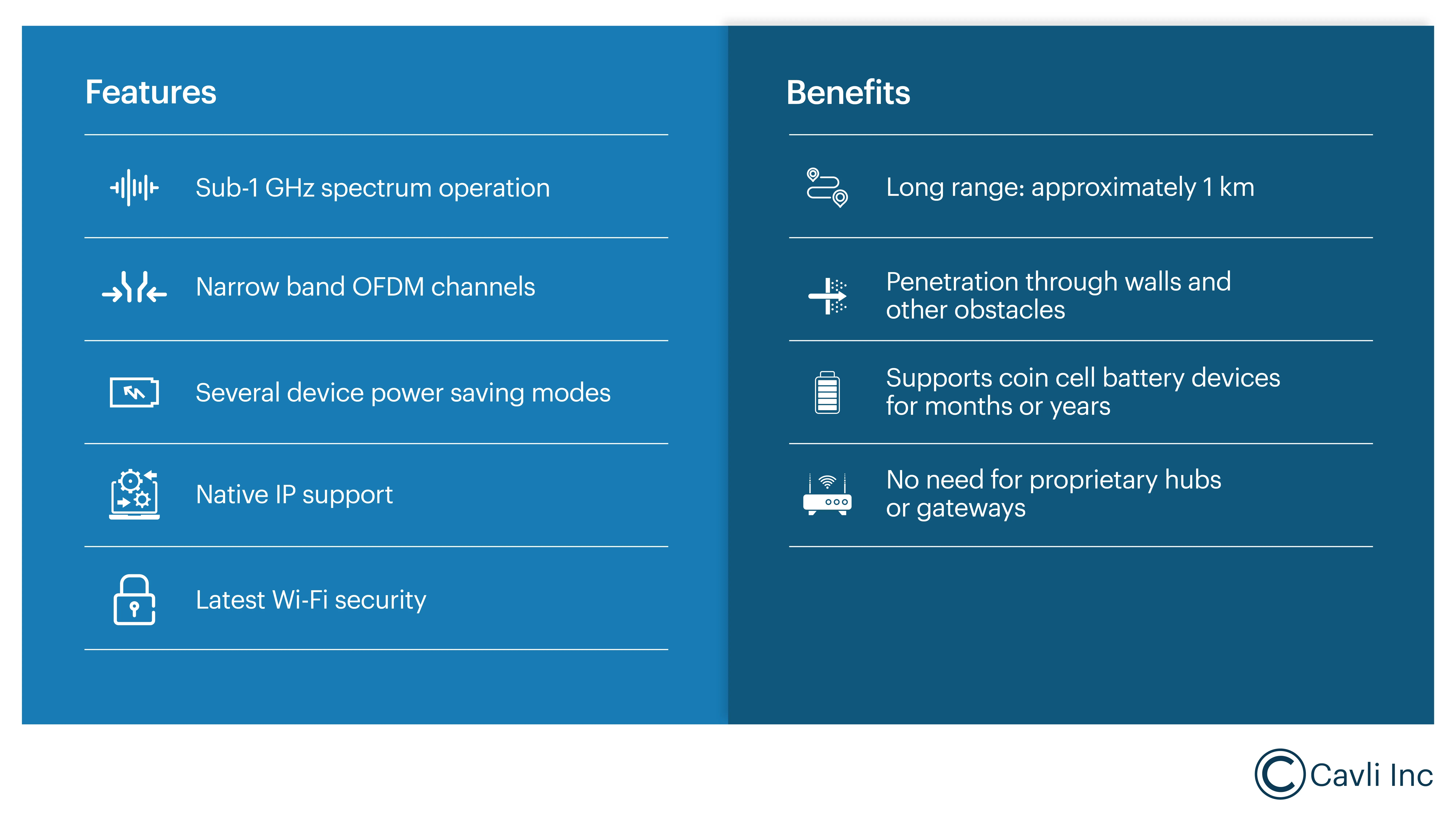
Sub-Gigahertz Operation
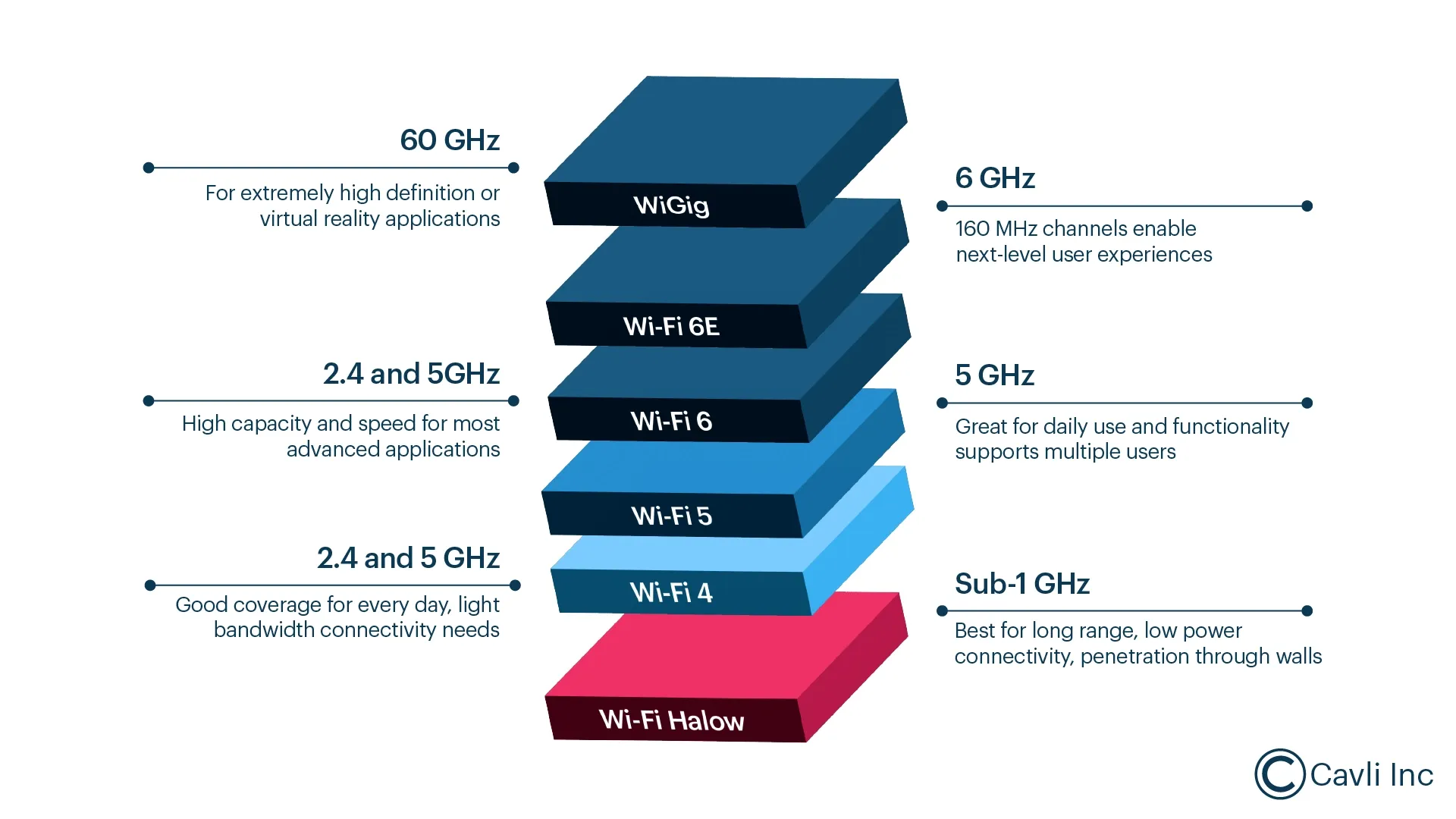
Unlike traditional Wi-Fi standards (such as Wi-Fi 6 and Wi-Fi 7), that operate in the crowded 2.4 GHz, 5 GHz, and 6 GHz bands, Wi-Fi HaLow uses a sub-1 GHz frequency. Wi-Fi HaLow offers a range of up to one kilometer (or even three kilometers in optimal conditions), making it ideal for connecting devices spread over large areas.
The Wi-Fi HaLow sub-1 GHz frequency band operation enables higher penetration through walls, floors, and other obstacles more effectively than higher-frequency bands. This capability allows it to maintain a strong signal over long distances, even in environments with physical barriers.
Device Capacity
Traditional Wi-Fi networks can struggle when too many devices attempt to connect to the same access point, often resulting in network congestion and performance issues. Wi-Fi HaLow is designed to support up to 8,000 devices per access point while consuming significantly less power. It allows IoT sensors and devices to operate efficiently for years on a single battery.
Extended Coverage
The extended range offered by Wi-Fi HaLow is invaluable for IoT applications that cover large areas, such as smart cities, agricultural fields, and industrial sites. Additionally, Wi-Fi HaLow supports narrow channel widths, enabling low data rates over long distances. It is ideal for IoT devices that transmit small amounts of data intermittently.
Mesh Networking
Wi-Fi HaLow can also support mesh networking, where multiple APs connect to extend the range and create a resilient network. It is particularly beneficial in environments like industrial sites, where signal coverage needs to be maintained even if one AP fails or loses connectivity.
No Proprietary Hubs or Controllers
Unlike other IoT technologies that may rely on proprietary hardware for network control, Wi-Fi HaLow eliminates the need for dedicated controllers or hubs. It not only simplifies deployment but also reduces long-term maintenance costs and lowers the total cost of ownership. Users can plug Wi-Fi HaLow APs into a traditional LAN, allowing HaLow clients to connect to the internet or other IP-based systems without any specialized gateways.
Why the Sub-1 GHz Frequency Matters in Wi-Fi HaLow
By operating in the sub-1 GHz range, Wi-Fi HaLow avoids interference from other devices that typically crowd the 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz bands. This interference reduction is crucial for environments like industrial sites or urban areas, where multiple networks and devices often compete for bandwidth. Furthermore, the lower frequency allows for a larger coverage area per access point, reducing the infrastructure needed to deploy a Wi-Fi HaLow network.
Wi-Fi HaLow is a connectivity solution engineered from the ground up for IoT, delivering long-range, high device capacity, and low power usage required for large-scale IoT deployments. As we move toward a future with billions of IoT devices, Wi-Fi HaLow stands out as a promising standard for connecting these devices seamlessly, reliably, and efficiently.
Infrastructure Components for Wi-Fi HaLow Connectivity
To deploy Wi-Fi HaLow, the core infrastructure requirements are similar to those of traditional Wi-Fi, with a few added benefits due to its extended range and unique features.
Wi-Fi HaLow Access Points (APs)
- Wi-Fi HaLow APs operate in the sub-1 GHz band, allowing them to cover larger areas when compared to standard Wi-Fi APs.
- Fewer APs are typically required to cover the same area, reducing infrastructure costs and simplifying deployment, particularly in large spaces like industrial sites or agricultural fields.
IoT Devices with Wi-Fi HaLow Support
- IoT sensors, cameras, and other devices should be Wi-Fi HaLow compatible to connect with HaLow APs. As the adoption of Wi-Fi HaLow amplifies, an increasing number of IoT devices are expected to include native support for this standard.
- Manufacturers are developing IoT devices optimized for HaLow’s low-power, long-range capabilities, making it easier for organizations to source compatible devices.
Integration with IP-Based Networks
- Wi-Fi HaLow Access Points connect to existing IP-based networks. It allows seamless integration with LAN or WAN setups, authorizing IoT data transmission to central servers, cloud platforms, and other devices.
- Organizations with Wi-Fi infrastructure can integrate Wi-Fi HaLow APs with minimal configuration, allowing them to expand IoT coverage without overhauling their entire network.
Key Considerations for Deployment of Wi-Fi HaLow
- Environmental Factors: Wi-Fi HaLow’s long-range and penetration capabilities allow it to work effectively in environments with barriers, such as warehouses, multi-floor buildings, or urban areas. Placement of APs, however, should consider any potential interference sources or physical obstacles to optimize connectivity.
- Bandwidth Requirements:Although Wi-Fi HaLow is designed for low-power, low data rate applications, it can also handle moderate data traffic, making it versatile. However, high-bandwidth applications may require traditional Wi-Fi or other connectivity solutions for reliable performance.
- Compliance with Regional Frequency Bands: Wi-Fi HaLow operates in the sub-1 GHz band, which may vary by region. Remaining compliant with local frequency regulations during deployment is essential, particularly for multinational organizations.
Comparison of Wi-Fi HaLow with Other LPWAN Technologies
As IoT networks expand, choosing the right connectivity technology becomes critical. While Wi-Fi HaLow offers impressive features, other Low-Power Wide-Area Network (LPWAN) technologies, such as LoRa, NB-IoT, Zigbee, and Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE), have also gained traction. Each of these technologies has distinct characteristics, and understanding their strengths and weaknesses compared to Wi-Fi HaLow can help determine the best solution for specific IoT use cases.
Wi-Fi HaLow vs. Traditional Wi-Fi
Traditional Wi-Fi protocols, like Wi-Fi 6 or Wi-Fi 5, are excellent for high-speed data transfer but fall short in range, power efficiency, and device capacity. Wi-Fi HaLow’s use of the sub-1 GHz band gives it a range advantage, allowing it to cover distances ten times greater than conventional Wi-Fi (up to 3 kilometers in ideal conditions). Additionally, while traditional Wi-Fi governs high-bandwidth applications like video streaming, Wi-Fi HaLow prioritizes low power consumption and extended range over speed. It is an ideal choice for battery-operated IoT devices that only need to transmit small data packets occasionally.
Wi-Fi HaLow vs. LoRa (Long Range)
LoRa is another popular LPWAN technology that operates in the sub-1 GHz range, providing long-range connectivity similar to Wi-Fi HaLow. However, LoRa’s data rate is considerably lower, typically around 300 bps to 50 kbps, making it unsuitable for applications requiring moderate data throughput. Wi-Fi HaLow, on the other hand, offers data rates up to 86.7 Mbps at shorter ranges, providing greater flexibility for applications that may need occasional bursts of higher bandwidth, such as video surveillance or advanced sensors.
Ideal Applications:
- LoRa: Best suited for low data rate applications, such as environmental monitoring and remote asset tracking.
- Wi-Fi HaLow: Suitable for applications requiring higher data rates and low latency, including video surveillance and industrial automation.
Wi-Fi HaLow vs. NB-IoT (Narrowband IoT)
NB-IoT, a cellular-based LPWAN technology, provides wide-area connectivity by operating on licensed spectrum bands. While NB-IoT offers an extensive range and strong security features, it often comes with higher costs due to data subscription fees, making it less attractive for large-scale IoT deployments. In contrast, Wi-Fi HaLow operates on unlicensed bands, making it a cost-effective solution for IoT applications without recurring fees.
Ideal Applications:
- NB-IoT: Suited for applications with guaranteed quality of service and coverage, such as emergency systems and healthcare monitoring.
- Wi-Fi HaLow: Ideal for scenarios where lower operational costs are essential, such as smart city infrastructure or agricultural IoT.
Wi-Fi HaLow vs. Zigbee and Z-Wave
Zigbee and Z-Wave are utilized in home automation and small-scale IoT deployments due to their low power consumption and mesh networking capabilities. However, their range is limited, typically covering less than 100 meters. Wi-Fi HaLow’s sub-1 GHz frequency provides a significantly extended range that would require multiple Zigbee or Z-Wave devices. Moreover, Wi-Fi HaLow’s ability to support thousands of devices on a single access point is a clear advantage in dense IoT environments where scalability is critical.
Ideal Applications:
- Zigbee/Z-Wave: Suited for home automation or localized sensor networks.
- Wi-Fi HaLow: Best suited for applications, covering large geographical areas or involving high device densities, such as smart cities or large industrial sites.
Wi-Fi HaLow vs. Zigbee and Z-Wave
Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE) is for short-range, low-power connections, particularly in personal devices and indoor IoT applications. However, BLE’s range is limited to approximately 50-100 meters, and it can only support a few connected devices before performance degrades. With an extended range and the ability to connect thousands of devices, Wi-Fi HaLow is better suited for large-scale IoT applications that require extensive connectivity across large areas.
Ideal Applications:
- BLE: Best for wearable devices, smart home appliances, and short-range communication.
- Wi-Fi HaLow: Ideal for industrial, agricultural, or municipal deployments where broader coverage is necessary.
| Attribute | Wi-Fi HaLow | LoRa | NB-IoT | Zigbee | BLE |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Frequency Band | Sub-1 GHz | Sub-1 GHz | Licensed spectrum | 2.4 GHz | 2.4 GHz |
| Range | Up to 3 km | Up to 10 km | Up to 10 km | Up to 100 m | Up to 100 m |
| Data Rate | Up to 86.7 Mbps | 300 bps - 50 kbps | 20 kbps - 127 kbps | Up to 250 kbps | 125 kbps - 2 Mbps |
| Device Capacity | 8,000 per AP | Limited by topology | Limited by network design | 65,000+ in mesh | Limited by topology |
| Ideal Use Cases | Smart cities | Environmental monitoring | Healthcare, emergency systems | Home automation | Wearable devices, smart home |
Limitations of Wi-Fi Halow Compared to Cellular Technologies
Coverage & Range
Wi-Fi HaLow has a limited range of up to 1 km and requires local access points for coverage. In contrast, NB-IoT, LTE, and 5G provide nationwide and global coverage, making them ideal for large-scale deployments without additional infrastructure.
Scalability & Device Density
Wi-Fi HaLow supports up to 8,191 devices per access point, suitable for localized deployments. On the other hand, Cellular IoT handles millions of devices per cell tower, making it the preferred choice for smart cities and large-scale industrial IoT.
Mobility & Roaming
Wi-Fi HaLow is designed for stationary or semi-mobile devices and requires handovers between access points. Cellular IoT provides seamless mobility across regions and networks, making it ideal for fleet tracking, autonomous vehicles, and logistics.
Power Consumption & Battery Life
Wi-Fi HaLow is power-efficient but still consumes more energy than NB-IoT and LTE-M, which offer a battery life of 10+ years. Cellular IoT enables ultra-low power applications like smart meters and remote sensors.
Infrastructure & Deployment Costs
Wi-Fi HaLow requires dedicated access points, increasing setup and maintenance costs. Cellular IoT uses existing telecom infrastructure, reducing upfront investment and making it more cost-effective for large-scale deployments.
Security & Network Reliability
Wi-Fi HaLow relies on Wi-Fi security protocols but is vulnerable to interference and local network attacks. Cellular IoT has SIM-based authentication, carrier-grade encryption, and dedicated security measures, making it more secure and reliable.
Latency & Data Rate
Wi-Fi HaLow offers moderate data rates (Mbps) with slightly higher latency than 5G. Cellular IoT varies: NB-IoT is optimized for low-data applications, while 5G offers ultra-low latency (~1 ms) for real-time applications like autonomous driving.
Advantages of Wi-Fi HaLow for IoT
As the Internet of Things (IoT) grows, the need for a connectivity solution that can handle the demands of thousands of devices operating over vast areas also heightens. Wi-Fi HaLow addresses several key pain points in connected technology and offers advantages that make it an ideal choice for IoT applications.
Reduced Infrastructure Costs
Wi-Fi HaLow offers an extensive range in vast area IoT applications—such as Smart Lighting, Environmental monitoring, or Asset Tracking across warehouses—without multiple repeaters or access points. It reduces infrastructure costs and simplifies network deployment, making it a practical and economical choice for large-scale IoT networks.
Power Efficiency for Long-Term Operation
Power consumption is a critical concern for IoT devices, many of which are battery-powered and need to operate for extended periods without frequent battery replacements.
Target Wake Time (TWT), the power-saving feature in Wi-Fi Halow, allows devices to "wake up" only when they need to transmit data, spending the rest of the time in a low-power sleep mode. By minimizing idle listening time, TWT ensures that each device only consumes power when actively communicating.
In addition to TWT, the Restricted Access Window (RAW) allows devices to communicate at scheduled times, minimizing power draw. As a result, IoT devices using Wi-Fi HaLow can achieve battery life spanning months or even years, making it ideal for sensors, meters, and other battery-powered devices that need to operate autonomously in remote or hard-to-reach locations where longevity is essential.
Increased Device Connections
Wi-Fi HaLow can support up to 8,000 devices on a single access point. For example, in a smart city scenario, a single Wi-Fi HaLow network could support connected streetlights, environmental sensors, public safety cameras, and parking meters—all within the same coverage area. This capability to support numerous devices without sacrificing performance makes Wi-Fi HaLow a powerful tool for building scalable IoT networks.
Reduced Interference for Reliable Connectivity
Operating in the sub-1 GHz range allows Wi-Fi HaLow to avoid much of the interference that plagues traditional Wi-Fi networks in the crowded 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz bands. It is particularly beneficial in environments where numerous networks and devices compete for bandwidth, such as urban areas or industrial sites. By reducing interference, Wi-Fi HaLow provides more reliable connectivity for IoT applications, ensuring that data transmission remains stable even in complex, high-density environments.
Enhanced Security for IoT Applications
Security is a top priority for IoT networks, especially in applications where sensitive data is transmitted, such as healthcare or industrial monitoring. Wi-Fi HaLow incorporates WPA3, the latest Wi-Fi security standard, which includes enhanced encryption and protection against cyber threats. It ensures that IoT networks using Wi-Fi HaLow are secure, even when deployed in critical applications.
Wi-Fi HaLow and IoT Applications
Industrial IoT (IIoT) Applications
Wi-Fi HaLow is ideal for industrial environments that require reliable, low-power connectivity over large areas.
Use Cases:
Asset Tracking:
- Monitor the movement of tools, equipment, and inventory across warehouses or manufacturing plants.
- Reduce losses and optimize workflows by integrating RFID and sensor-based tracking.
Predictive Maintenance:
- Connect sensors to industrial machinery to monitor vibration, temperature, and wear and tear.
- Prevent costly downtime by detecting failures before they occur.
Worker Safety:
- Use smart wearables and environmental sensors to detect hazardous conditions in factories, mines, and construction sites.
- Ensure compliance with safety regulations and enhance emergency response.
Smart Agriculture & Environmental Monitoring
Wi-Fi HaLow’s long-range capabilities make it a perfect choice for smart farming and environmental IoT applications.
Use Cases:
Crop Monitoring:
- Deploy soil sensors to measure moisture levels, temperature, and nutrient content across large fields.
- Optimize irrigation and fertilization using real-time data.
Livestock Tracking:
- Use Wi-Fi HaLow-enabled collars for monitoring the location, health, and movement of livestock.
- Reduce losses and improve farm management.
Climate & Weather Monitoring:
- Insight collection on temperature, humidity, wind speed, and rainfall for better crop yield predictions.
- Deploy remote weather stations powered by Wi-Fi HaLow.
Smart Cities & Infrastructure
Wi-Fi HaLow can be used in large-scale IoT deployments to enhance urban infrastructure.
Use Cases:
Traffic Management:
- Connect sensors and smart cameras to optimize traffic lights, reduce congestion, and monitor road conditions.
- Enable real-time vehicle-to-infrastructure (V2I) communication.
Public Safety & Security:
- Deploy long-range surveillance cameras, access control systems, and emergency alert devices.
- Improve law enforcement response times with real-time data sharing.
Utility Management:
- Use Wi-Fi HaLow to remotely monitor and control streetlights, water meters, and energy grids.
- Reduce energy consumption and improve operational efficiency.
Smart Homes & Building Automation
Wi-Fi HaLow can improve energy efficiency and security in residential and commercial buildings.
Use Cases:
Energy Management:
- Connect smart thermostats, HVAC systems, and lighting to reduce power consumption.
- Enable remote control of home appliances and devices.
Security & Surveillance:
- Use Wi-Fi HaLow to integrate smart locks, security cameras, motion detectors, and alarms.
- Extend network coverage across large buildings without expensive infrastructure.
Smart Appliances & IoT Devices:
- Enable wireless control of refrigerators, washing machines, and other appliances.
- Improve user experience with IoT-enabled automation.
Healthcare & Medical IoT
Wi-Fi HaLow can support secure, reliable connectivity for healthcare applications and remote patient monitoring.
Use Cases:
Patient Monitoring:
- Connect wearable health devices, glucose monitors, and ECG sensors to track patient vitals.
- Enable real-time alerts for medical staff.
Medical Equipment Connectivity:
- Ensure seamless data transmission between MRI scanners, ventilators, and hospital networks.
- Reduce downtime and improve diagnostics.
Elderly & Assisted Living:
- Use Wi-Fi HaLow-enabled fall detection sensors, emergency response systems, and smart wearables.
- Provide remote patient monitoring for seniors and chronically ill patients.
Retail & Smart Warehousing
Retailers and logistics providers can use Wi-Fi HaLow to improve inventory management, customer experience, and warehouse automation.
Use Cases:
Inventory & Supply Chain Tracking:
- Using RFID tags and sensors to track goods across warehouses and distribution centers.
- Reduce inventory loss and optimize stock levels.
Smart Checkout & POS Systems:
- Enable seamless mobile payments, self-checkout systems, and AI-powered customer interactions.
- Reduce queue times and improve customer satisfaction.
In-store analytics & Digital Signage:
- Track customer movement and preferences to optimize store layouts and marketing strategies.
- Enable real-time updates on digital signage displays.
Closing Notes
Wi-Fi HaLow (IEEE 802.11ah) is a long-range, low-power Wi-Fi solution designed for IoT applications that require better coverage and power efficiency than traditional Wi-Fi. Operating in the sub-1 GHz spectrum, it offers superior obstacle penetration, extended range (up to 1 km), and support for thousands of devices per access point, making it ideal for IoT, smart agriculture, and smart buildings.
However, Wi-Fi HaLow lacks the global coverage, mobility, and seamless roaming offered by NB-IoT, LTE, and 5G. Wi-Fi HaLow requires local access points, making it a cost-effective choice for private networks but unsuitable for large-scale mobile applications. While HaLow is perfect for localized, high-density IoT networks, NB-IoT and LTE-M remain the best options for global, low-power, wide-area applications. Choosing the right technology depends on range, power efficiency, scalability, and security needs, ensuring IoT deployments are efficient, scalable, and future-proof.


