What is MQTT Protocol?
MQTT (Message Queuing Telemetry Transport) is a lightweight, open-source messaging protocol designed for efficient communication in IoT (Internet of Things) applications. It uses a publish/subscribe model, ensuring low-bandwidth, high-reliability communication between devices. MQTT is widely used for real-time data exchange, enabling scalable and secure connectivity in smart homes, industrial automation, and other connected systems. Its simplicity and support for various transport layers make it ideal for resource-constrained devices in remote or unreliable network environments.
In the world of IoT (Internet of Things), communication protocols play a crucial role in enabling device interaction. The MQTT protocol, or Message Queuing Telemetry Transport, is one of the leading IoT protocols that has revolutionized the efficiency of data exchange between IoT devices. Designed for low-bandwidth, high-latency environments, the MQTT protocol in IoT is ideal for smart and connected systems.
In this blog let’s explore how MQTT communication became the most reliable mode of communication in the connected world. This blog covers:
- MQTT Architecture
- MQTT publish/ subscribe model
- MQTT Servers/brokers
- MQTT client and server communication
- MQTT Message Types and Format
- MQTT Security
- Popular MQTT brokers and clients and lastly MQTT use cases in various applications.
Recent Developments in MQTT Usage in IoT: "As of 2024, the landscape of IoT devices globally includes approximately 16.7 billion devices, with projections indicating this number could reach 25.4 billion by 2030."
MQTT Protocol: A Key Player in Communication Protocols in IoT
The MQTT full form is Message Queuing Telemetry Transport, a pivotal communication protocol within the landscape of IoT protocols. As a lightweight and efficient messaging protocol, the MQTT protocol is designed to handle communication between devices in environments where bandwidth is limited and network reliability is often inconsistent. This makes it an ideal solution for IoT applications that require real-time data exchange with minimal power consumption.
The MQTT protocol in IoT utilizes a publish/subscribe model, setting it apart from other traditional IoT protocols that rely on request/response communication methods. In this architecture, IoT devices (clients) either publish data to a central MQTT broker or subscribe to specific topics to receive information. This decoupled communication model enhances scalability and efficiency of data transmission, enabling seamless integration of multiple IoT devices in complex networks. The lightweight nature of the MQTT protocol in IoT makes it an essential part of communication protocols in IoT , facilitating efficient data transfer across various IoT networks. Its simplicity and low overhead help reduce network bandwidth requirements, ultimately minimizing costs, making it one of the preferred IoT protocols for developers.
By incorporating the MQTT protocol in IoT projects, developers can create robust, scalable, and efficient communication networks, allowing for effective data transmission even in environments with constrained resources. This makes the MQTT protocol an essential component of the IoT protocol stack, widely adopted across various industries such as smart home automation, industrial IoT, and remote monitoring systems.
How MQTT Protocol in IoT Works:
Publish/Subscribe Model of MQTT Protocol
The MQTT Protocol operates on a publish/subscribe architecture, where devices (clients) either publish messages to a broker or subscribe to receive messages from the broker. This model is particularly suited for IoT because it ensures seamless communication even when the network is unreliable or has low bandwidth.
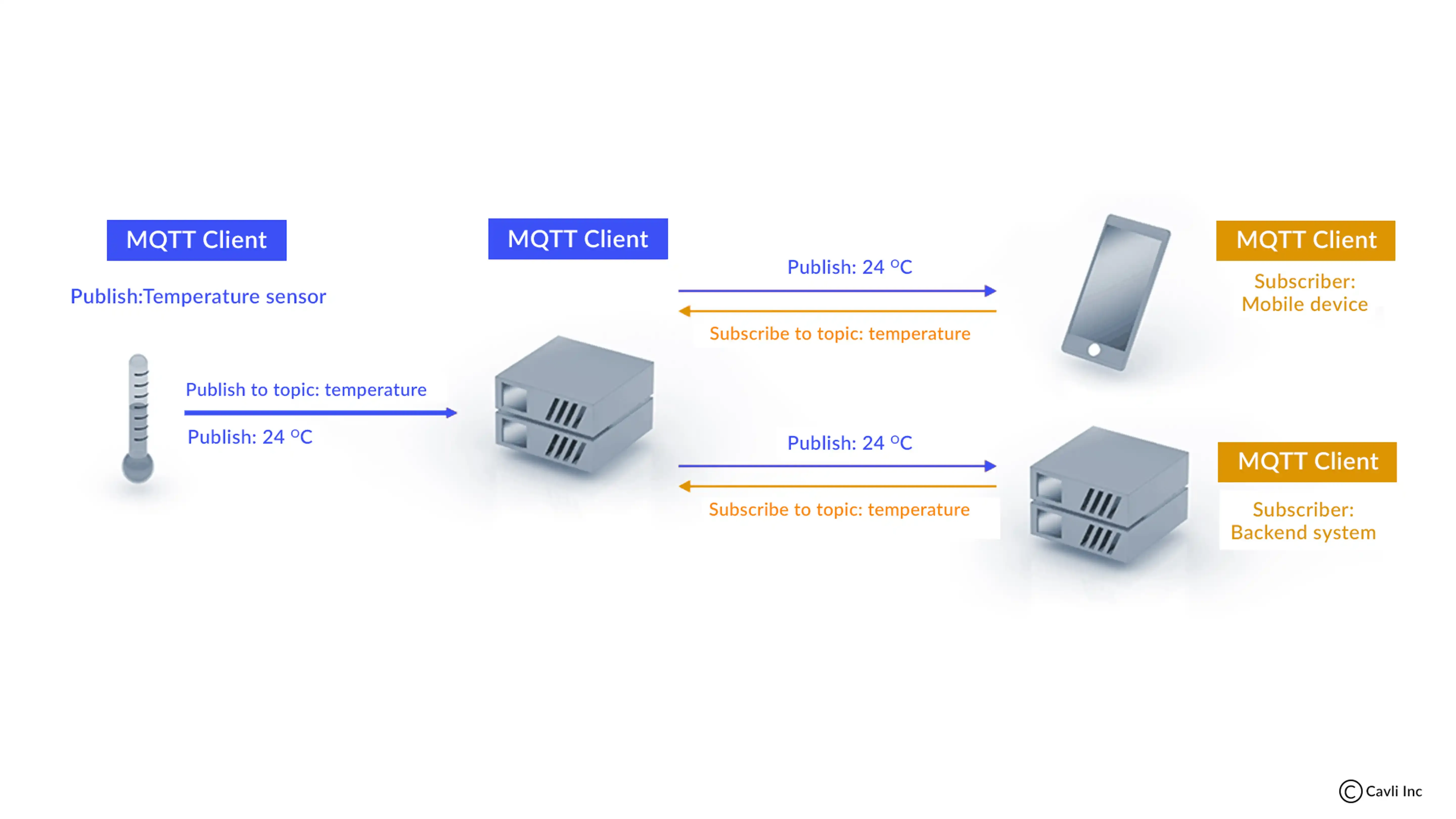
Publish/Subscribe Model of MQTT Protocol
Message Flow:
When a publisher device sends a message, the broker (central communication point) distributes it to all subscribed clients. This decouples the devices, allowing them to communicate without maintaining a direct connection, which is vital in large-scale IoT deployments.
Quality of Service (QoS) Levels in MQTT Protocol for IoT Applications
The MQTT protocol is a cornerstone of communication protocols in IoT, recognized for its adaptability and efficiency in managing diverse communication requirements. By offering three distinct Quality of Service (QoS) levels, the MQTT protocol in IoT ensures reliable data transmission. This flexibility allows developers to select the QoS level best suited to their application's needs, enhancing the overall performance of IoT systems.
QoS 0: "At Most Once" – Lightweight and Efficient
QoS 0 is the simplest form of data transfer under the MQTT protocol. It works in a "fire-and-forget" manner, offering minimal overhead, with no delivery guarantees or acknowledgment of message receipt. This makes it well-suited for IoT applications where low latency and high efficiency are prioritized, such as environmental monitoring or real-time sensor data where occasional data loss is acceptable.
QoS 1: "At Least Once" – Balanced Reliability
With QoS 1, the MQTT protocol guarantees that a message reaches its intended recipients at least once, even though duplicates may occur. The broker acknowledges each message with a PUBACK, ensuring reliability. This level of service is widely used in industrial IoT, smart metering, and predictive maintenance where guaranteed message delivery is needed, but duplicate data can be tolerated and managed.
QoS 2: "Exactly Once" – Absolute Reliability
QoS 2 provides the most reliable level of message delivery, ensuring that each message is delivered only once and without duplication. It uses a four-step handshake process, ensuring rigorous data integrity. This makes QoS 2 an ideal choice for mission-critical IoT protocols like financial transactions, asset tracking, or command-and-control systems where data accuracy is essential.
Optimizing QoS Levels for IoT Deployments
When selecting a QoS level for the MQTT protocol in IoT, consider factors like:
- Network Reliability: For environments with unstable networks, QoS 1 or 2 helps ensure data delivery but may increase bandwidth requirements.
- Message Frequency and Size: QoS 0 is efficient for high-frequency data with small payloads, while QoS 1 or 2 works better for larger, critical updates.
- Latency Needs: QoS 0 minimizes latency and is suitable for applications where rapid data transfer matters most.
The QoS levels in MQTT protocol allow developers to effectively optimize communication protocols in IoT depending on the specific use case, balancing reliability and resource efficiency. Whether it's lightweight IoT applications with QoS 0 or high-integrity systems with QoS 2, the MQTT protocol remains a vital component of the IoT protocol stack, providing the versatility and reliability needed for modern connected systems.
Architectural Components of MQTT Protocol in IoT Deployments
The MQTT protocol in IoT has a set of components. The 4 major MQTT components are
- MQTT Message
- MQTT Client
- MQTT Server or Broker
- MQTT Topic
MQTT Message
MQTT messages are made up of three parts:
- Fixed header
- Variable header
- Payload
The fixed header contains information about the type of message and the quality of service level.
The variable header contains information that is specific to each message type.
The MQTT message consists of a payload containing the actual message data published by a client. MQTT protocol limits the maximum payload size to 256 MB per message.
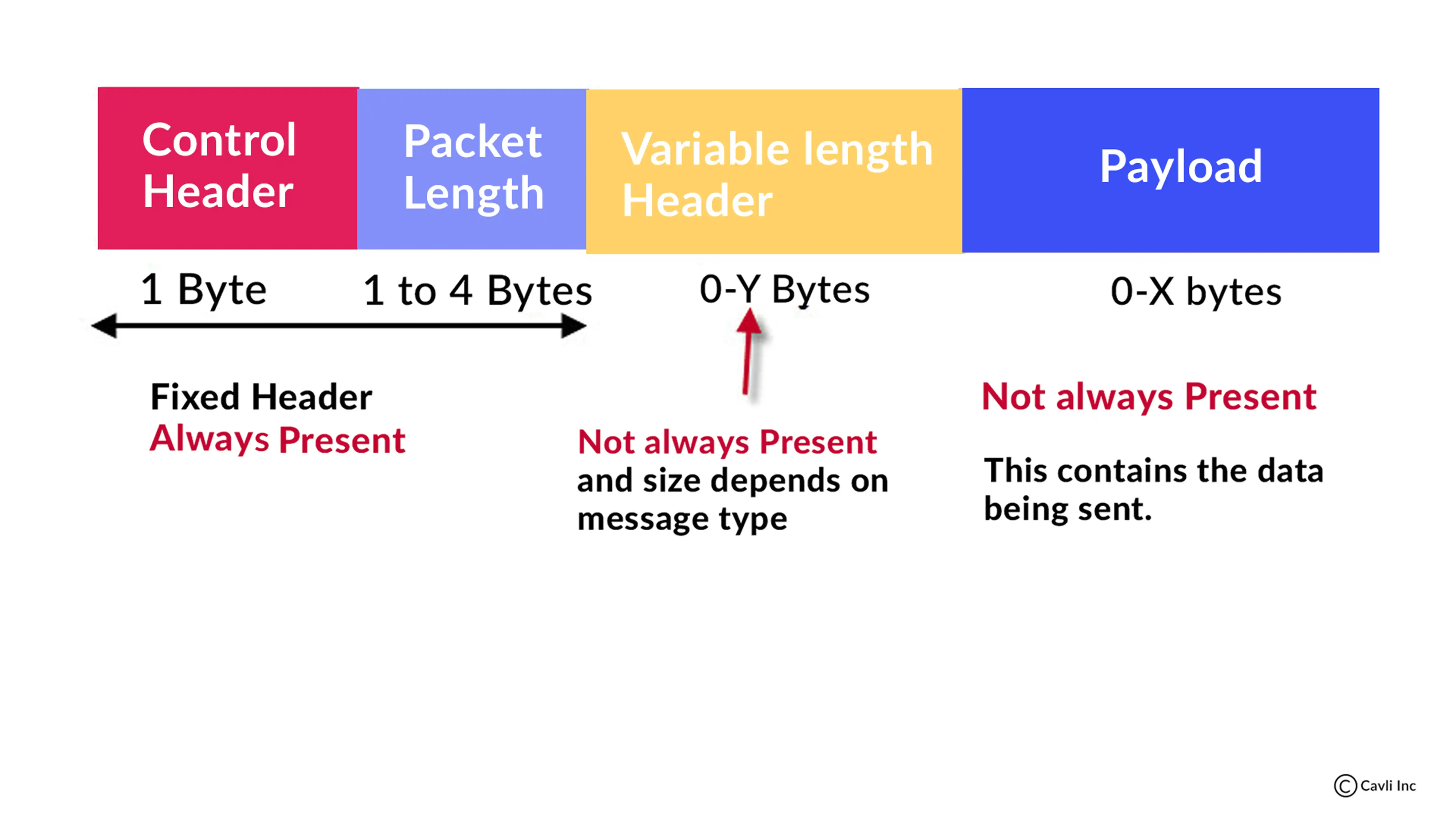
MQTT Message Structure
Persistent Sessions
Persistent sessions allow an MQTT client’s state to be maintained by the broker across connections. This feature is particularly beneficial in scenarios where devices intermittently connect and disconnect due to network instability.
Case Study: In industrial remote monitoring, sensors deployed in harsh environments may experience frequent disconnections. Persistent sessions ensure that data continuity is maintained, and no critical alerts are lost during periods of disconnection.
Retained Messages
Retained messages ensure that the most recent message on a topic is stored by the broker and delivered to any new subscribers immediately upon subscription.
Example: In a warehouse monitoring system, the latest temperature reading can be retained so that new devices subscribing to the temperature topic receive the most recent data without waiting for the next update.
Types of MQTT Messages
The three most common MQTT message types are crucial for managing data flow and maintaining connections within the MQTT protocol in IoT systems. Each type plays a distinct role in the communication process:
Connect:
This message establishes the initial connection between the MQTT client and the server. In the MQTT protocol in IoT, the Connect message sets up parameters for a stable and reliable connection.
Disconnect:
The Disconnect message allows the MQTT client to complete any pending tasks before severing the TCP/IP connection. This is critical for ensuring that all data transmission is properly concluded, maintaining system integrity, and preventing data loss.
Publish:
After transmitting the message to the MQTT client, the Publish command resumes the application thread instantly. It handles the distribution of telemetry data among devices and ensures that messages are delivered according to the defined quality of service levels, essential for the reliability of IoT applications.
Subscribe:
To establish one or more topic subscriptions, a Subscribe packet is delivered from the client to the server. This message type enables clients to express interest in specific topics and receive updates whenever new data is published, enhancing the dynamism and responsiveness of IoT systems.
What are MQTT Clients?
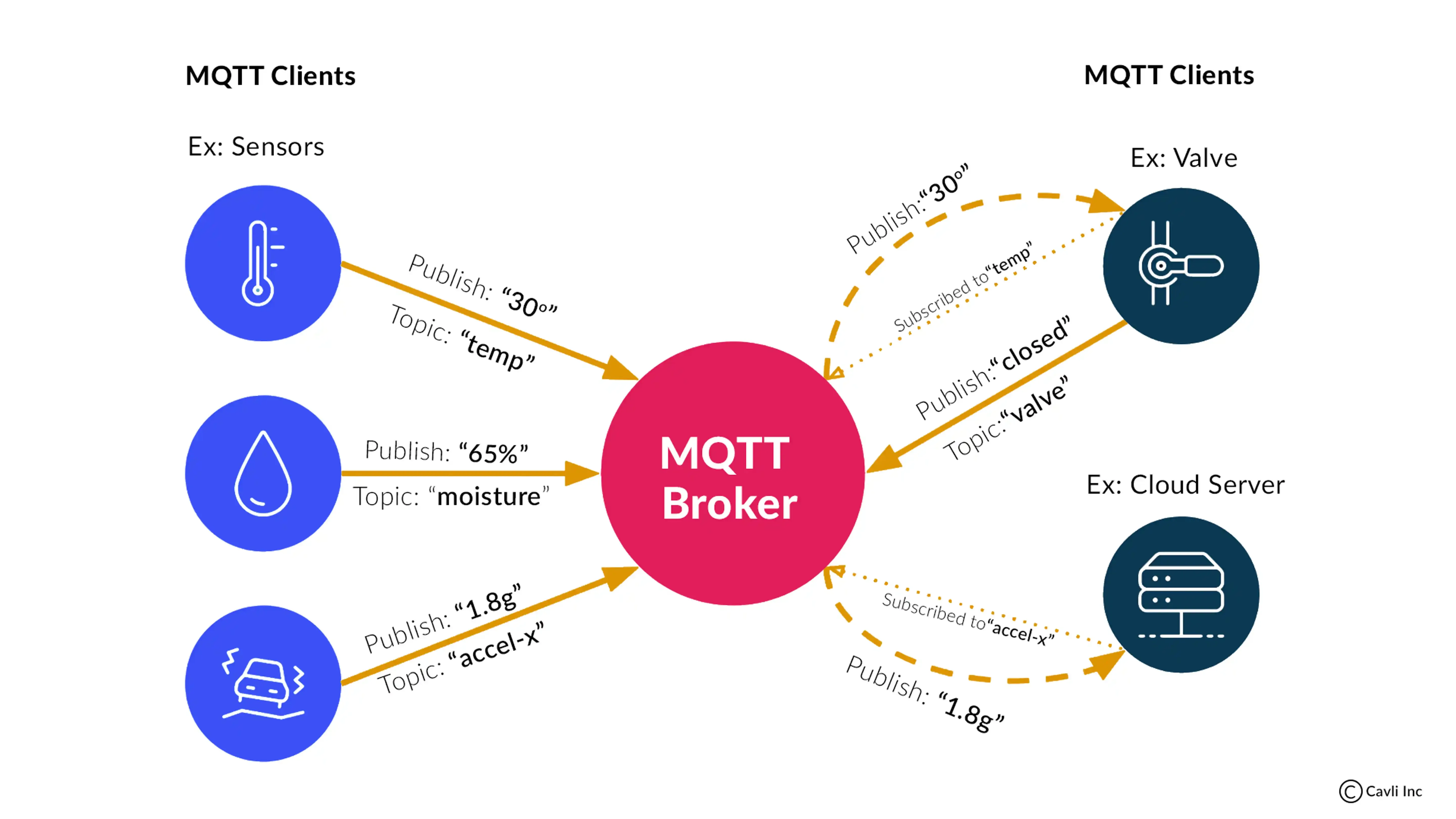
MQTT Clients
MQTT clients can be categorized into two main roles: publishers and subscribers.
Publishers:
These are MQTT clients that send or "publish" messages to the MQTT broker. Messages published by publishers are typically associated with specific topics. Topics are like message channels, and messages are sent to a particular topic.
Subscribers:
These are MQTT clients that receive or "subscribe" to messages from the MQTT broker. Subscribers express their interest in specific topics, and the broker sends messages published to those topics to the subscribing clients.
With the publish/subscribe model, clients do not need to know about each other. They only need to know the topic that they are interested in. When a client publishes a message to a topic, the message is delivered to all of the clients that have subscribed to that topic.
What is MQTT Broker?
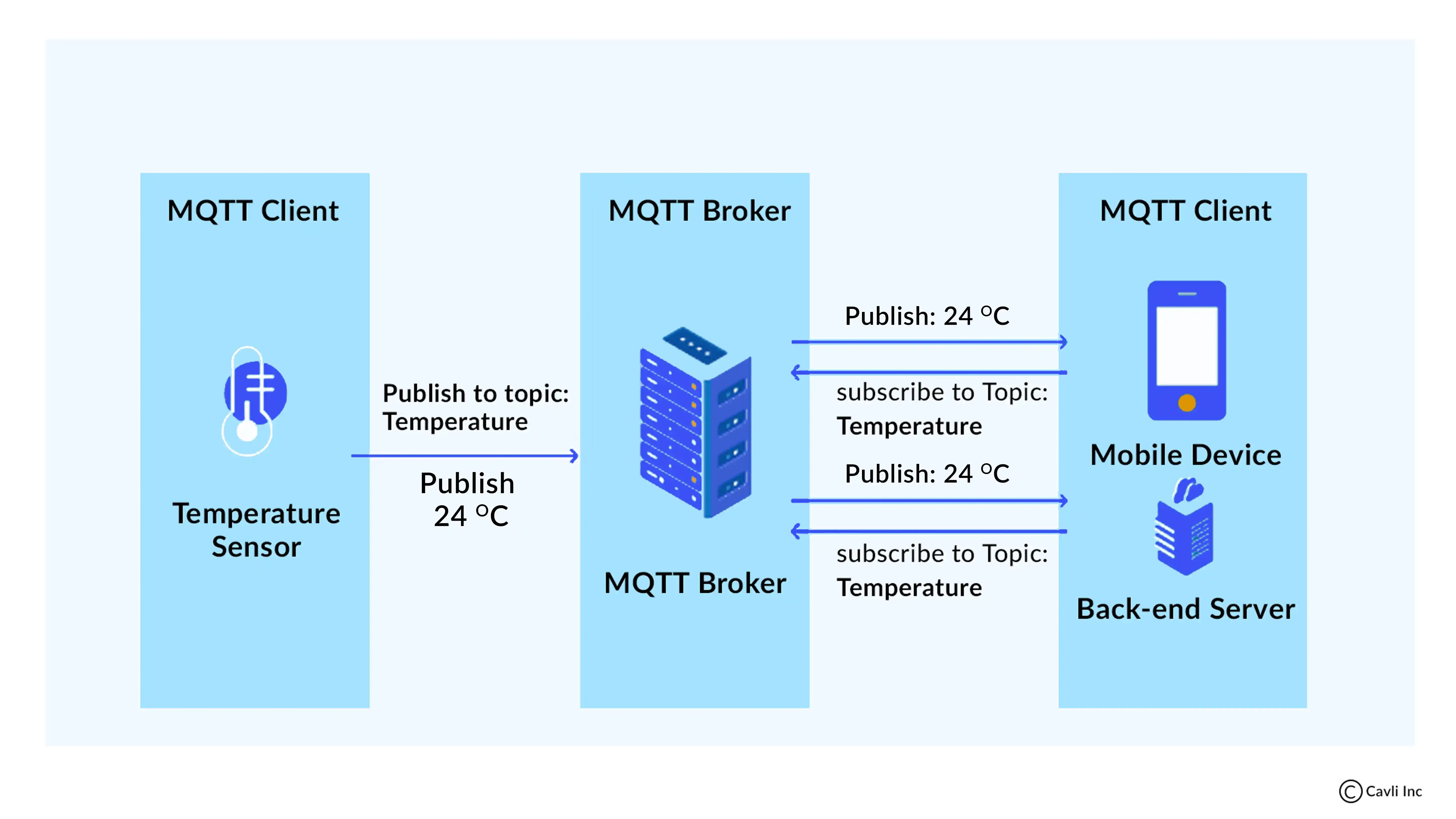
MQTT Broker
An MQTT broker is a server that receives all messages from the clients and then routes these messages to the appropriate destination clients. As a central hub in the MQTT protocol, the broker manages message queues, topic subscriptions, and every MQTT connection, ensuring seamless device communication. It also handles the authentication and authorization of clients, ensuring secure and efficient communication in an MQTT network.
MQTT Topic
MQTT Topic is a UTF-8 string that brokers use for message filtering. Topics are represented as hierarchical strings separated by forward slashes. Clients publish messages to specific topics. Subscribers register interest in topics and receive published messages matching those topics. The broker handles routing messages from publishers to the appropriate subscribed clients based on topic filtering.
Example of Topic
My_home/first_floor/dining_room/temperature
Topics are used to define the path of the message. Here the message (temperature) will be sent to the dining room which is on the first floor of the home.
Emerging Trends in MQTT Technology for IoT: "Integration of MQTT with AI and Machine Learning: The convergence of IoT and AI, with MQTT at the core, is integral to the growth of the projected $236-billion IoT market. This integration facilitates smarter decision-making processes across various sectors."
Advanced Features of MQTT 5 Protocol and Its Role in IoT Platforms
MQTT 5, the latest version of the MQTT protocol, introduces several enhancements that significantly improve its functionality and adaptability in diverse IoT ecosystems. This section outlines the key features of MQTT 5 and explores its integration into contemporary IoT platforms.
Key Enhancements in MQTT 5
Shared Subscriptions
This feature allows multiple clients to subscribe to the same topic and share the message load, which can be particularly useful in large-scale deployments where message volume can be very high.
Message Property Expansion
MQTT 5 includes a wide range of message properties like response topic, content type, correlation data, and more, allowing better handling and routing of messages based on their content and purpose.
Enhanced Authentication Mechanisms
With MQTT 5, support for enhanced authentication mechanisms has been added, including challenge/response style authentication, which provides an additional layer of security.
Request/Response Pattern
Unlike its predecessors, MQTT 5 supports a native request/response mechanism that simplifies the implementation of synchronous communication patterns within asynchronous MQTT workflows.
Improved Error Reporting
MQTT 5 provides more detailed error reporting at the protocol level, which helps in better diagnostics and troubleshooting of communication issues.
Edge Computing and 5G Integration with MQTT in IoT: "The advancement of MQTT in IoT, coupled with edge computing and 5G, is set to revolutionize real-time data processing and connectivity, critical for applications such as autonomous vehicles and smart cities."
Integration into New IoT Platforms
Smart Home Systems
Utilizing MQTT 5's shared subscriptions and request/response patterns, smart home platforms can manage device states more efficiently and respond to user commands more promptly.
Industrial IoT (IIoT) Applications
In industrial contexts, the expanded message properties and improved error handling are crucial for managing complex machinery and processes where reliability and timely data transmission are critical.
Healthcare Devices
The enhanced security features of MQTT 5 make it suitable for sensitive healthcare applications, ensuring that data transmission between devices and monitoring systems is secure and compliant with regulatory standards.
Industry Adoption of MQTT Protocol: "Significant industries such as manufacturing and healthcare are increasingly leveraging the MQTT protocol in IoT to enhance operational efficiency and improve patient care. Specifically, MQTT is pivotal for monitoring manufacturing equipment for predictive maintenance and for tracking medical equipment in healthcare settings."
Working of MQTT Protocol in IoT Explained
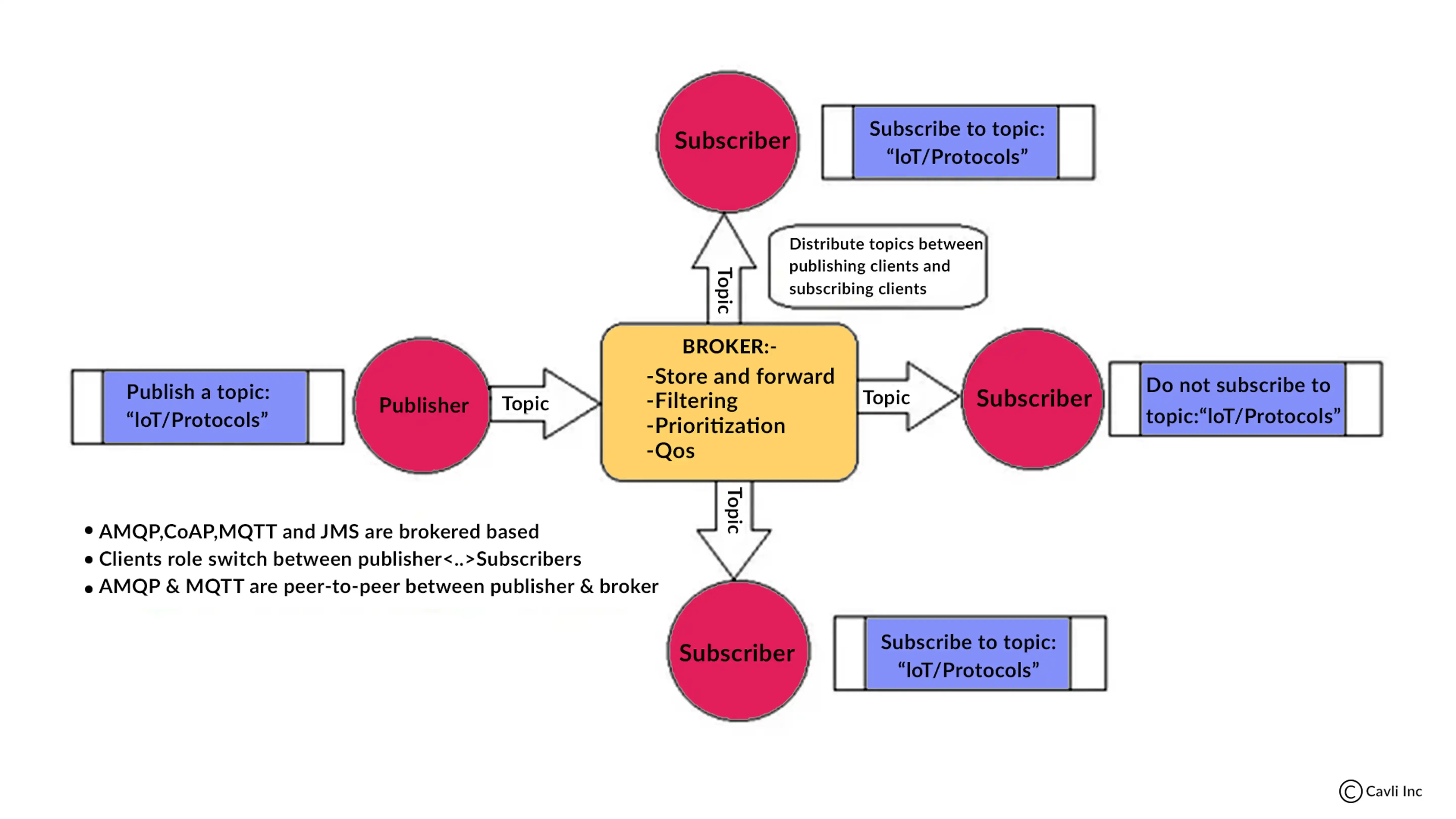
Working of MQTT
When a client establishes an MQTT connection with a broker, it must first identify itself, ensuring secure communication. This is done using the MQTT connect packet. The connect packet contains the client's name, the broker's name, and the security credentials (if any).
Once the client has connected to the broker, it can start publishing and subscribing to messages.
To publish a message, the client sends an MQTT publish packet. The publish packet contains the message's topic, the message's payload, and the message's QoS (quality of service).
To subscribe to a topic, the client sends an MQTT subscribe packet. The subscribe packet contains the topic that the client wants to subscribe to.
When a client publishes a message, the broker delivers the message to all of the clients that have subscribed to the topic.
When a client subscribes to a topic, the broker starts delivering messages that are published to that topic.
Understanding MQTT Security in IoT Communication Protocols
The MQTT Protocol in IoT is widely used for its lightweight and efficient communication, but security is paramount when dealing with sensitive IoT data. The protocol offers robust security mechanisms to ensure the integrity, confidentiality, and authenticity of data exchanged between MQTT clients and brokers. Key security components include authentication, authorization, encryption, and data integrity, which safeguard MQTT communications against unauthorized access and potential cyber threats.
1. Authentication: Verifying Device Identity in the MQTT Protocol
Authentication is the first line of defense in the MQTT protocol in IoT, safeguarding every MQTT connection by ensuring that only verified devices can access the broker securely. By verifying the identity of each client, MQTT minimizes the risk of unauthorized access and prevents malicious devices from infiltrating the network.
Username and Password Authentication:
The most common method involves configuring a username and password for each MQTT client. While straightforward, this approach should always be used in conjunction with encrypted communication (e.g., TLS/SSL) to prevent credential interception.
Best Practice: Use strong, unique credentials and avoid hardcoding them within the device firmware to enhance security.
Client Certificate Authentication:
For more secure environments, MQTT can leverage X.509 certificates for mutual authentication. In this setup, both the client and broker authenticate each other using digital certificates, ensuring a high level of trust.
Implementation: The broker requires a Certificate Authority (CA) to verify client certificates, providing stronger assurance of device identity and reducing the risk of impersonation attacks.
Token-Based Authentication:
Advanced MQTT deployments may utilize token-based authentication methods, such as OAuth 2.0. Tokens provide a more scalable and flexible approach to managing device authentication, especially in large IoT networks with dynamic connections.
Use Case: OAuth tokens are ideal for IoT applications where devices frequently connect and disconnect, ensuring secure and dynamic access control.
2. Authorization: Controlling Access to MQTT Topics and Resources
After successful authentication, the MQTT Protocol enforces authorization to control what actions an authenticated client can perform. Authorization ensures that clients have the correct permissions to publish or subscribe to specific MQTT topics, thus preventing unauthorized access or modification of sensitive data.
Topic-Based Access Control:
The broker manages access permissions at the topic level, allowing administrators to define precise rules that restrict which topics a client can publish or subscribe to. This is crucial in multi-tenant IoT environments where different devices require access to different data streams.
Example: A temperature sensor might have permission to publish data to "factory/sensor/temperature" but should be restricted from subscribing to "factory/control/commands" to prevent unintended actions.
Role-Based Access Control (RBAC):
Many MQTT brokers support Role-Based Access Control, where clients are assigned roles (e.g., admin, subscriber, publisher) with predefined permissions. This method streamlines the management of access rights in large-scale IoT deployments.
3. Transport Layer Security (TLS/SSL): Securing MQTT Communication Channels
Transport Layer Security (TLS) or Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) is essential for encrypting the communication channel between MQTT clients and the broker, ensuring data privacy and protection against eavesdropping or man-in-the-middle attacks.
TLS Handshake Process:
During the TLS handshake, the client and broker exchange digital certificates and encryption keys to establish a secure communication channel. This process ensures both parties are who they claim to be, and the data transmitted is encrypted.
TLS Versions: It is recommended to use the latest version of TLS (TLS 1.2 or TLS 1.3) for enhanced security and to avoid vulnerabilities present in older versions.
Mutual TLS Authentication:
For maximum security, MQTT supports mutual TLS, where both the client and broker present certificates for verification. This dual authentication strengthens the trust between communicating parties, making it extremely difficult for unauthorized devices to gain access.
4. Payload Encryption: Enhancing Data Confidentiality in MQTT Protocol
While TLS/SSL encrypts data during transmission, payload encryption offers an additional layer of security by encrypting the actual message content (payload) within the MQTT messages.
End-to-End Encryption (E2EE):
In scenarios where end-to-end encryption is necessary, the message payload is encrypted by the publisher before being sent to the broker and remains encrypted until it reaches the subscribing client. This ensures that even if the broker is compromised, the message content remains secure.
Encryption Standards: Common algorithms used for payload encryption include AES-256, RSA, and ECC (Elliptic Curve Cryptography), which offer robust protection for sensitive data.
Implementing Payload Encryption:
Payload encryption requires manual encryption and decryption on the client side, often using libraries like OpenSSL or other cryptographic frameworks. This provides more granular control over data security, especially in environments where sensitive information is transmitted (e.g., financial transactions, healthcare data).
Best Practices for Securing the MQTT Protocol in IoT Applications
- Always Use TLS/SSL: Ensure that all MQTT communications are encrypted using TLS/SSL, especially when transmitting sensitive data.
- Employ Strong Authentication Methods: Use certificate-based authentication or token-based systems over simple username/password combinations for enhanced security.
- Implement Fine-Grained Authorization: Regularly audit and manage topic permissions to prevent unauthorized access.
- Monitor and Log MQTT Traffic: Utilize monitoring tools to detect any unusual activity or potential breaches in the MQTT network.
Enhanced Security Measures for MQTT: "To address the rising security challenges, there is an increasing focus on bolstering hardware security through embedded chipset protections in MQTT devices. This ensures data integrity from edge devices to the cloud, safeguarding the communication protocols in IoT."
Applications of MQTT Protocol in IoT Systems
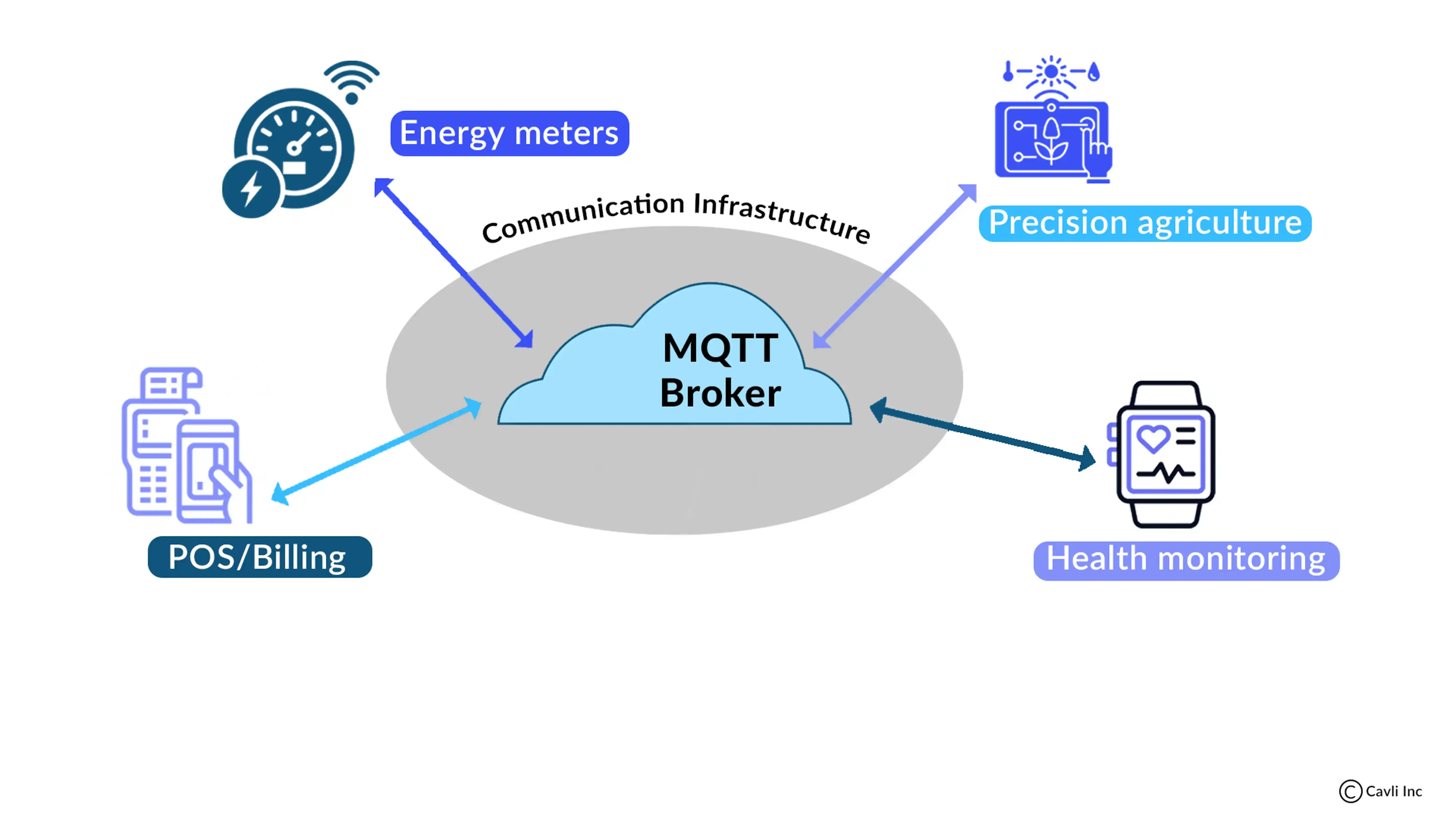
MQTT Applications
The MQTT protocol in IoT is frequently used in smart home automation, healthcare, agriculture and industrial IoT. Among IoT protocols, MQTT is favored due to its reliability and efficiency in real-time applications.
In smart energy grids, MQTT enables the real-time transmission of meter readings, ensuring accurate customer billing. This efficiency in data transmission highlights the capabilities of the MQTT protocol in IoT.
In precision agriculture, the MQTT protocol in IoT enables reliable monitoring of soil moisture sensors and crop health analytics, even in farmlands with unstable connectivity. Maintaining a robust MQTT connection ensures farmers receive timely alerts on droughts or pest infestations, which helps protect yields and resources.
For device health monitoring, MQTT facilitates continuous remote monitoring by instantly transmitting data such as vibration and temperature to operators. This enables teams to identify deteriorating components and prevent unplanned downtime, demonstrating the effectiveness of the MQTT protocol in IoT.
In billing and invoicing systems, MQTT enhances accuracy and auditability. Its reliable message delivery, coupled with duplicate detection, transforms invoice processing for telcos, utilities, and SaaS companies. By eliminating duplicate records, the MQTT protocol in IoT prevents costly inaccuracies and revenue leakage.
Learn More: Top 7 IoT Applications in 2024
Download Now: Comprehensive Guide to Smart Farming and Agriculture 2024
Download Now: Smart Health Monitoring
Smart Agriculture with MQTT: "In smart agriculture, the MQTT protocol facilitates robust communication among IoT devices and decision-making systems, significantly enhancing farm management. However, addressing MQTT's security vulnerabilities is crucial to protect against potential cyber threats in these communication protocols."
Advantages of MQTT Protocol in Communication Protocols for IoT
Ease of Use
One of the most compelling features of MQTT is its ease of use. The MQTT protocol offers ready-made clients and brokers, allowing for quick and straightforward implementation. This simplicity greatly facilitates the integration of IoT devices into networks, minimizing development time and simplifying connectivity challenges.
Reliability
MQTT queues messages and retries delivery, effectively handling intermittent connections that are common in IoT environments. Its Quality of Service (QoS) levels add another layer of reliability, ensuring that messages are delivered accordingly. This reliability is critical for maintaining data integrity and timely delivery across diverse and potentially unstable network conditions.
Bidirectional Communication
MQTT supports omnidirectional communication, meaning any device in the network can act as a publisher or a subscriber to any topic. This flexibility enhances communication within IoT networks, enabling devices to both send and receive important operational data. This bidirectional nature of MQTT facilitates more dynamic and interactive IoT applications.
Scalability and Future-Proofing
MQTT handles broadcasting a message to a hundred devices or a million effortlessly. The process remains the same: publish to a common topic, and all subscribed devices receive the message. This scalability makes MQTT an excellent choice for growing IoT networks, accommodating an increasing number of devices without needing significant changes to the infrastructure.
Comprehensive Comparison of MQTT, HTTP, CoAP, and AMQP Protocols for IoT Communication
| Feature/Comparison | MQTT | HTTP | CoAP | AMQP |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Protocol Type | Lightweight messaging protocol | Application layer protocol | Lightweight application protocol | Message-oriented middleware |
| Communication Model | Publish/Subscribe | Request/Response | Request/Response | Publish/Subscribe |
| Message Delivery Reliability | Quality of Service (QoS) levels ensure reliable delivery | No built-in QoS | Limited reliability | High reliability with store-and-forward |
| Overhead | Minimal overhead, highly efficient | Higher overhead due to headers and state | Lightweight | Relatively high overhead |
| Connectivity | Works well in low-bandwidth, intermittent, or unstable networks | Requires stable and persistent connections | Designed for constrained devices | Requires stable, high-bandwidth connections |
| Security | TLS encryption, username/password-based authentication | HTTPS for encryption | DTLS for security | TLS encryption, supports fine-grained access control |
| Scalability | High scalability for IoT environments | Limited scalability for many small devices | Good scalability for constrained networks | Highly scalable, suitable for complex systems |
| Device Suitability | Best for battery-constrained, resource-limited devices | Suitable for devices with higher resources | Suitable for constrained IoT devices | Suitable for enterprise-level systems |
| Use Case Examples | Smart homes, industrial automation, healthcare monitoring | Web-based applications, RESTful APIs | Simple IoT deployments like smart meters | Financial transactions, supply chain systems |
| Payload Format | Binary, application-specific | Text-based (JSON, HTML) | Binary or text-based | Binary, application-specific |
| Protocol Standardization | OASIS Standard | IETF RFC 2616 (HTTP/1.1) | IETF RFC 7252 | AMQP 1.0 (ISO/IEC 19464) |
| Performance in IoT | Highly optimized for IoT | Poor for constrained devices | Designed specifically for IoT | Not optimized for constrained IoT devices |
| Implementation Complexity | Easy to implement and lightweight | Medium complexity | Low complexity | High complexity |
| Support for Retained Messages | Supported | Not supported | Not supported | Supported |
| Best For | IoT sensor networks, large-scale deployments, low-power environments | Traditional web applications, less dynamic environments | Constrained networks, lightweight tasks | Enterprise-grade messaging with complex needs |
Future Outlook for MQTT in IoT: "The IoT sector is undergoing transformative changes, with MQTT at the forefront, driving continuous evolution and resilience through technological advancements and strategic shifts. The integration of AI into industrial automation, the rise of generative AI in manufacturing, and the adoption of DataOps solutions are among the key trends contributing to a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 17% in the IoT market through 2030."
Closing Notes on the MQTT Protocol for IoT Communication
In the fast-paced IoT domain, MQTT communications is ideal for IoT applications. With its publish/subscribe model, it unlocks the full potential of IoT in a wide variety of industries, ranging from health monitoring to manufacturing and many more. Leverage this simple architecture and easy-to-use API of MQTT to ensure reliable connectivity and optimum performance in our connected ecosystem.
To learn more, visit us at
https://www.cavliwireless.com/iot-modules/cellular-modules
Download Now: 2024 Comprehensive Guide to Message Query Telemetry Transport (MQTT)


