James, Jr. Network Engineer
Hey, I was diving into the 5G implementation and it's impressive that mmWave's theoretical peak speed is up to 10 Gbps. Is this really achievable in the real world scenario?
Adam, Network Engineer
Yes, but reaching peak speeds in real-world scenarios is challenging. mmWave offers excellent capacity and potentially delivers Gigabit speeds (up to 1 Gbps) under ideal conditions. However, the limited range (approximately 500 meters under line-of-sight conditions) and penetration issues through buildings hinder consistent high speeds in urban environments.
James, Jr. Network Engineer
That makes sense. What could be the possible alternative? Does Sub-6 GHz offer a better balance in this regard?
Adam, Network Engineer
Absolutely. Sub-6 GHz provides a more balanced solution. It offers wider coverage (up to several kilometers) and better building penetration, even though its speeds are typically lower, ranging from 100 to 400 Mbps. It ensures consistent connectivity especially in suburban and rural settings.
James, Jr. Network Engineer
I read that Beamforming and Massive MIMO can improve mmWave performance. Are we considering these for our urban deployments?
Adam, Network Engineer
Definitely! Beamforming and Massive MIMO technologies enhance mmWave's signal strength and directionality. These techniques have the potential to improve overall mmWave performance and make it more suitable for scalable IoT deployments. To know more about mmWave and Sub-6 GHz specifications, continue reading the blog.
Introduction
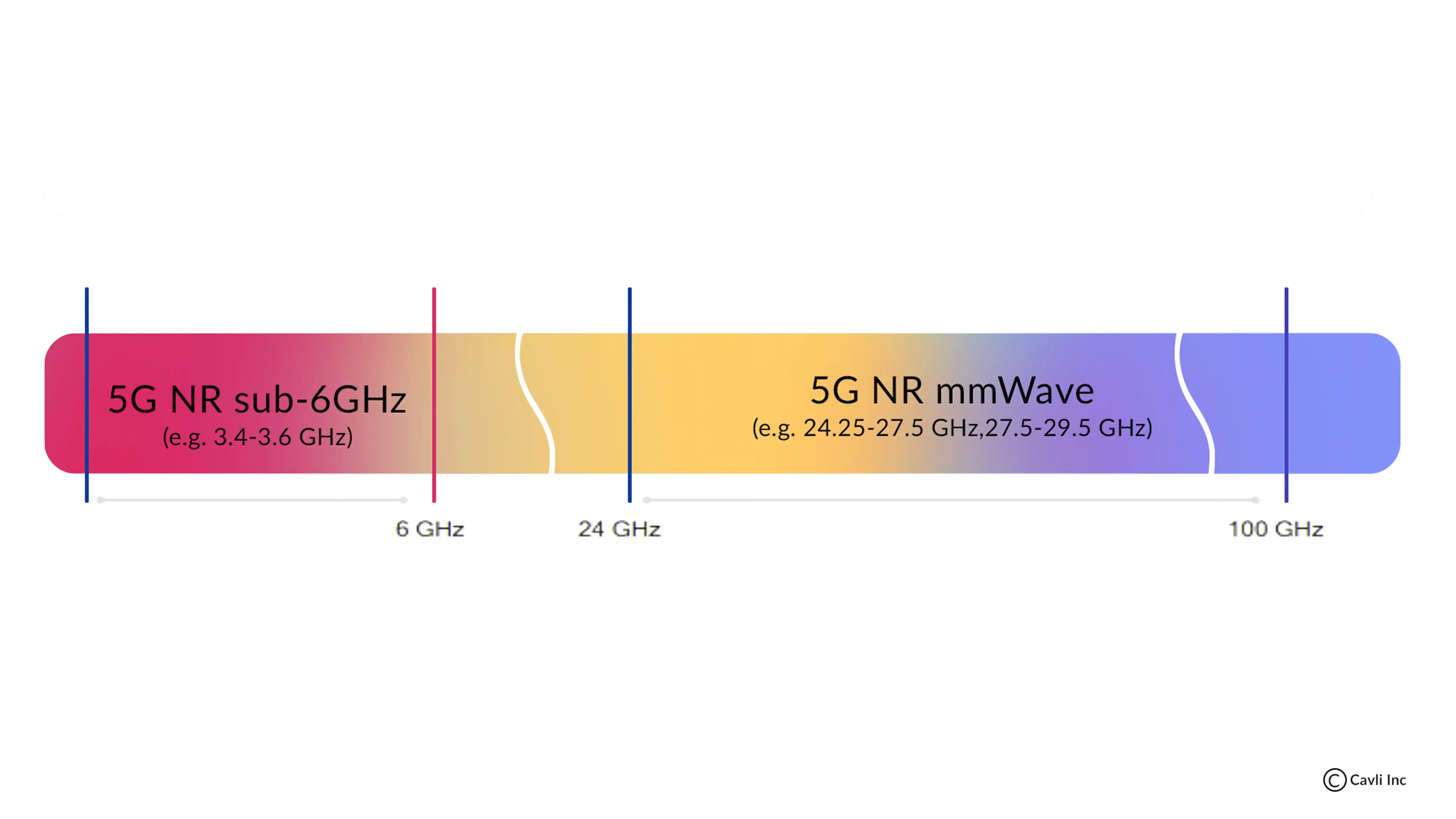
With the introduction of 5G - the 5th generation of wireless, the mobile communications devices and the data usage is skyrocketing. The 5th Gen networks are said to bring a massive change in the congestion experienced in the communication networks. The improvement of spectrum capacity in 5G networks is one of the major advancements to address this situation. The 5G networks are designed to work well in between the 1 GHz to 6 GHz ( Sub-6 GHz) and the unused band above 24 GHz( mmWave).
5G Spectrum
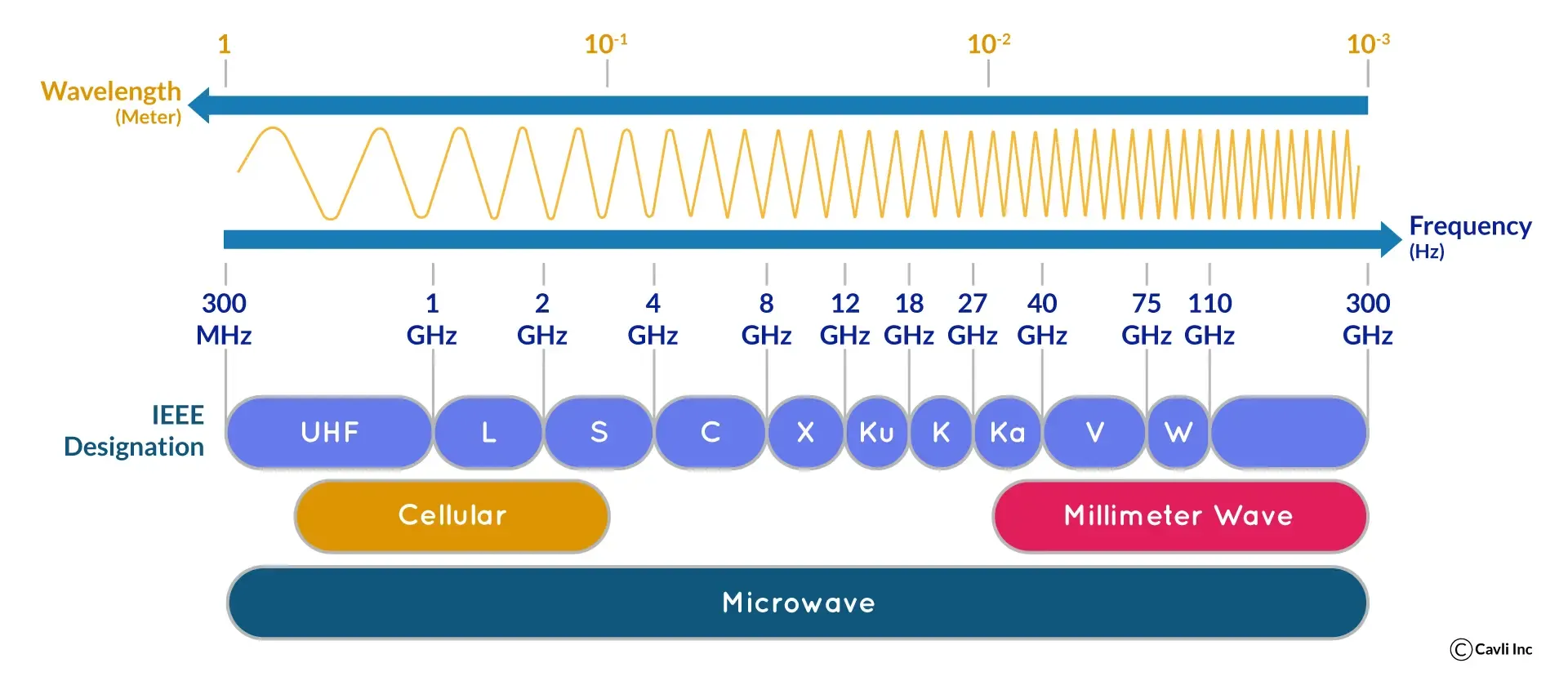
The 5G spectrum encompasses a wide range of radio frequencies that are pivotal for transmitting data over cellular networks under the fifth-generation technology standard. These frequencies are meticulously categorized into distinct bands, each with unique characteristics essential for realizing the full potential of 5G's high-speed, low-latency, and extensive connectivity capabilities.
Frequency Range 1 (FR1):
FR1, often referred to as Sub-6 GHz, spans lower frequency bands from 410 MHz up to 7.125 GHz. This range incorporates several bands previously utilized by legacy cellular technologies like 3G and 4G, alongside newly allocated bands specifically designated for 5G. This segment of the spectrum is crucial for widespread coverage and enhanced penetration, making it ideal for urban and suburban environments where extensive reach is required.
Frequency Range 2 (FR2):
FR2, or the millimeter wave (mmWave) bands, includes the higher frequencies from 24.25 GHz to 71.0 GHz. These mmWave frequencies are renowned for their ability to deliver data at significantly higher speeds and with remarkably lower latency compared to Sub-6 GHz. The mmWave spectrum is particularly advantageous in dense urban settings or areas requiring high capacity, such as stadiums and concert venues. Due to its high frequency, mmWave 5G offers unparalleled data transmission capabilities, enabling advanced applications like real-time augmented reality, ultra-HD video streaming, and more.
What is Sub-6 GHz?
Sub-6 GHz, designated as the frequency range between 1 GHz and 6 GHz on the electromagnetic spectrum, is also known as FR1. It has played a foundational role in the development of earlier wireless communication technologies, including 2G, 3G, LTE, and Wi-Fi. With the ongoing retirement of older cellular networks, Sub-6 GHz is being re-farmed to support the rollout of advanced 5G technologies such as 5G NR (New Radio) and 5G RedCap (Reduced Capability). This transition is critical for enhancing the efficiency and capacity of global 5G networks. The Sub-6 GHz bands are particularly valued for their balance of coverage and bandwidth, making them ideal for providing robust 5G connectivity across both urban and rural areas. This spectrum facilitates lower latency and higher throughput, essential for applications requiring real-time data transfer, such as autonomous vehicles, industrial IoT, and complex machine-to-machine communications. As 5G technology evolves, the strategic importance of Sub-6 GHz continues to grow, driving advancements in network architecture to support an expanding array of 5G-enabled services and infrastructure.
What is 5G mmWave?
5G mmWave, often referred to as millimeter wave, taps into a previously unused high-band of frequencies known as FR2, spanning from 24 GHz to 71.0 GHz. This technology leverages mm wave frequencies to provide enormous spectrum capacity and rapid data transmission over short distances, ideal for dense urban environments. The deployment of mmWave 5G is crucial for supporting high-demand applications requiring vast bandwidth, such as ultra-HD video streaming, immersive augmented reality experiences, and extensive IoT networks. As mmWave technology evolves, it continues to transform the landscape of mobile communications by offering unprecedented data speeds and network efficiency.
Difference Between 5G mmWave and Sub-6 GHz
| Feature | 5G mmWave | Sub-6 GHz |
|---|---|---|
| Frequency Range | Above 24 GHz (typically 24 GHz to 100 GHz) | Below 6 GHz |
| Bandwidth | Very high (up to several GHz) | Lower (tens to hundreds of MHz) |
| Data Transfer Rates | 1 Gbps | 100-700 Mbps |
| Coverage Area | Short range; typically less than a kilometer | Wider area; can cover several kilometers |
| Penetration & Propagation | Poor (struggles with buildings, rain, etc.) | Better (can penetrate walls and buildings) |
| Deployment | Urban areas, stadiums, and indoor environments | Urban, suburban, and rural areas |
| Capacity | Very high (supports high user density) | Moderate (lower than mmWave) |
| Use Cases | High-speed broadband, AR/VR | Mobile broadband, IoT, wide-area coverage |
| Infrastructure Requirement | Dense network of small cells | Less dense, traditional cell towers |
| Latency | Very low | Low (but typically higher than mmWave) |
| Cost | High (due to dense infrastructure needs) | Lower (due to wider coverage per cell) |
| Device Compatibility | Limited (not all devices support mmWave) | Widespread (most modern devices support Sub-6 GHz) |
| Standardization | More complex due to higher frequencies | More mature and widely adopted |
| Security | Potentially more vulnerable to signal interference | Generally less susceptible to interference |
Nomenclature of 5G Frequency Bands
The nomenclature of 5G spectrum bands using an "n" prefix comes from the 3rd Generation Partnership Project (3GPP), which is a collaboration between groups of telecommunications standards associations. The "n" stands for "new radio" (NR), which is the standard for 5G networks. These identifiers are prefixed to differentiate it from earlier generations of mobile technology, such as 4G LTE (where bands are usually prefixed with "B" or "LTE").
The "n" prefix helps in distinguishing 5G bands and their corresponding frequencies and characteristics, making it easier for manufacturers, service providers, and regulators to communicate about and manage 5G technology and deployment.
Nomenclature of FR1 Bands
| Band | Duplex mode | ƒ (MHz) | Common name |
|---|---|---|---|
| n1 | FDD | 2100 | IMT |
| n2 | FDD | 1900 | PCS |
| n3 | FDD | 1800 | DCS |
| n5 | FDD | 850 | CLR |
| n7 | FDD | 2600 | IMT-E |
| n8 | FDD | 900 | Extended GSM |
| n12 | FDD | 700 | Lower SMH |
| n14 | FDD | 700 | Upper SMH |
| n18 | FDD | 850 | Lower 800 (Japan) |
| n20 | FDD | 800 | Digital Dividend (EU) |
| n25 | FDD | 1900 | Extended PCS |
| n28 | FDD | 700 | APT |
| n29 | SDL | 700 | Lower SMH |
| n30 | FDD | 2300 | WCS |
| n34 | TDD | 2100 | IMT |
| n38 | TDD | 2600 | IMT-E |
| n39 | TDD | 1900 | DCS-IMT Gap |
| n40 | TDD | 2300 | S-Band |
| n41 | TDD | 2500 | BRS |
| n48 | TDD | 3500 | CBRS (US) |
| n50 | TDD | 1500 | L-Band |
| n51 | TDD | 1500 | L-Band Extension |
| n65 | FDD | 2100 | Extended IMT |
| n66 | FDD | 1700 | Extended AWS |
| n70 | FDD | 2000 | AWS-4 |
| n71 | FDD | 600 | Digital Dividend (US) |
| n74 | FDD | 1500 | Lower L-Band (Japan) |
| n75 | SDL | 1500 | L-Band |
| n76 | SDL | 1500 | Extended L-Band |
| n77 | TDD | 3700 | C-Band |
| n78 | TDD | 3500 | C-Band |
| n79 | TDD | 4700 | C-Band |
| n80 | SUL | 1800 | DCS |
| n81 | SUL | 900 | Extended GSM |
| n82 | SUL | 800 | Digital Dividend (EU) |
| n83 | SUL | 700 | APT |
| n84 | SUL | 2100 | IMT |
| n86 | SUL | 1700 | Extended AWS |
| n89 | SUL | 850 | CLR |
| n90 | TDD | 2500 | BRS |
- FDD - Frequency Division Duplex
- TDD - Time-Division Duplexing
- SDL - Supplementary Downlink
- SUL - Supplementary Uplink
Nomenclature of FR2 Bands
| Frequency Range 2 | ||
|---|---|---|
| Band | ƒ (GHz) | Common name |
| n257 | 26 GHz and 29 GHz | LMDS (Local multipoint distribution service) |
| n258 | 24.25-27.5 GHz | K-band |
| n260 | 39 | Ka-band |
| n261 | 28 | Ka-band |
Countries and Their 5G Frequency Bands
| Country | Frequency Bands |
|---|---|
| North America | Assigned n71, n66, n2, n41, n5, n12, n25, n48, n78, n258, n260, n261 |
| Canada | Multiple bands in commercial deployment such as 600 MHz, 3.5 GHz, and other mobile bands using DSS. Looking to open 3.9 GHz band and 26, 28, and 38 GHz bands for exclusive use. Above 95 GHz bands for unlicensed operations. |
| Europe | Assigned n78, n28A, n8, n20, n38, n1, n3, n7, n75/76, n257, n258 |
| UK | Assigned 3.4-3.8, 3.8-4.2 for private networks. 26 GHz, 40 GHz authorization framework under definition. |
| Germany | Assigned 3.4-3.7 GHz, 3.7-3.8 GHz for private networks. 26 GHz licenses issued on demand on a local basis. |
| France | Assigned 3.4-3.8 GHz. Test licenses for 26 GHz band. |
| Italy | Assigned 3.4-3.8 GHz and 26 GHz. |
| China | Assigned 41+,79,1,3,78. |
| South Korea | Assigned n78, n257. |
| Japan | Assigned n77, n78, n79, n1, n3, n257. |
| India | Assigned spectrum across all bands for 5G, including 600, 700 MHz, 3.4-3.67 MHz and 26 GHz. 800, 900 MHz,1.8, 2.1, 2.3, and 2.5 GHz bands currently used for 4G, but expected to become 5G bands. |
| Australia | Assigned 3.4-3.7 GHz. 3.7-4.2 GHz, 4.4-4.5 GHz, 4.8-5.0 GHz under on-going consultation. 26 GHz mmWave band for local licensing and wide-area allocation. |
Learn More About the Cavli 5G RedCap IoT Module
Benefits of mmWave 5G
5G mmWave technology, operating in the mm wave frequencies, dramatically enhances wireless communication with its ability to deliver the fastest 5G speeds and ultra-low latency. This is crucial in densely populated areas where mmWave's highly localized coverage can significantly improve enterprise and urban infrastructure efficiency. The deployment of small cells is integral in extending mmWave 5G's reach, particularly indoors, where high-frequency mmWave signals may struggle with penetration due to modern building materials.
5G mmWave Use Cases
Cities like New York and Boston are pioneers in leveraging mmWave 5G for smart city applications, enhancing everything from public safety to transportation systems with real-time, high-definition data capabilities. In the business realm, private 5G networks utilizing mmWave technology offer unmatched performance and network control, crucial for powering IoT applications and real-time analytics in sectors such as manufacturing and logistics. This facilitates a significant enhancement in operational efficiency and decision-making processes, critical in today's fast-paced industrial environments.
Learn More: Top 7 IoT Applications in 2024
Closing Notes
The integration of 5G mmWave and Sub-6 GHz technologies enables a versatile, robust network infrastructure capable of supporting a wide range of use cases, from urban to rural settings, ensuring that the diverse needs of consumers, businesses, and industries are met with unprecedented levels of wireless communication performance.
Amusing Tech Chronicles
Facts and Anecdotes related to this edition of Wireless By Design
![]()
Gleam v/s Laser Beam
Sub-6 GHz can be compared to sunlight passing through clouds. It spreads widely, covering a large area and is fairly consistent. Meanwhile, 5G mmWave is like a laser beam: extremely focused, very powerful, and can transmit a lot of energy (data) but only in a very narrow and direct line.
![]()
Highway System
Think of Sub-6 GHz like a series of highways with multiple lanes (broader coverage) but with a speed limit. It allows more vehicles (data) to travel at a good pace but not at the highest possible speeds. Conversely, 5G mmWave is like a separate track built for extremely high speeds.
![]()
Broadcast Radio v/s Wi-Fi Signal
Imagine Sub-6 GHz as a broadcast radio signal, it travels long distances and penetrates through buildings and reaches a wide audience. On the other hand, 5G mmWave is like a Wi-Fi signal offering high bandwidth and faster data rates but with a much shorter range and cannot easily penetrate obstacles.
Go Beyond and Explore
Is C-band and mmWave the same?
C-band refers to a specific segment of the electromagnetic spectrum that is used in telecommunications. In the context of 5G, C-band typically refers to the frequency range of approximately 4 GHz to 8 GHz, but most commonly, the term is used to denote frequencies around 3.7 GHz to 4.2 GHz, especially for cellular networks. It offers a balance between coverage and capacity with moderate data speeds and is used for wider area coverage compared to mmWave. It is considered a "mid-band" spectrum in the context of 5G networks.
Do environmental factors affect the propagation of 5G mmWave and Sub-6 GHz?
Environmental factors, such as terrain, building materials, and weather conditions, can differently impact mmWave and Sub-6 GHz frequencies. Sub-6 GHz waves can better penetrate obstacles and are less affected by weather. mmWave frequencies are more susceptible to attenuation and blockage. Effective integration requires network designs that account for these differences, ensuring reliable connectivity by dynamically switching between mmWave and Sub-6 GHz based on environmental conditions and user mobility.
What types of applications are best served by Sub-6 GHz frequencies?
Sub-6 GHz frequencies are ideal for a broad range of applications, including smart cities, connected homes, industrial automation etc. This band can support services that require wide-area coverage, such as in rural or suburban areas, and is suitable for applications that need reliable connectivity but not necessarily the extreme speeds offered by mmWave.


