James, Jr. Network Engineer
Hi Adam, I recently heard, on a global scale, regions such as India, the US, and Southeast Asia are leading the way in adoption of 3GPP's 5G standalone (SA) standard and are expected to gain momentum from 2024. I would like to know how 5G networks have gained this upper hand when compared to their predecessors?
Adam, Network Engineer
Absolutely, James! The demand for 5G communication is indeed on the rise, and there are several reasons why 5G networks have a significant edge over previous generations like 4G. One of the biggest changes is the shift to a cloud-native architecture. 5G core networks are designed to run in cloud environments using containerized microservices. This is a big departure from 4G's EPC, which was more of a monolithic structure running on dedicated hardware.
James, Jr. Network Engineer
That’s a great point to start with. Does 5G Core add in new capabilities helping in enhancing the network performance and efficiency?
Adam, Network Engineer
The 5G Core brings several new capabilities that significantly improve network performance and efficiency. Key among them are Network Slicing, virtualization, and CUPS (Control and User Plane Separation). Network Slicing allows us to create multiple virtual networks on a shared physical infrastructure, each tailored for specific use cases or services, while Virtualization utilizes NFV (Network Function Virtualization), enabling network functions to run as software on common, off-the-shelf hardware instead of specialized hardware. Also, dynamic resource allocation optimizes usage of network resources, reducing costs, and making the network more agile.
James, Jr. Network Engineer
I know there are even more 5G capabilities that keep the communication in 5G networks more efficient. What are the benefits these 5G architectural advantages impart to the IoT applications?
Adam, Network Engineer
The 5G architecture brings several benefits that significantly enhance IoT applications, each tailored to different requirements and use cases. For example, a slice for smart city infrastructure (like traffic lights or surveillance cameras) can be optimized for high reliability and moderate bandwidth, while another slice for massive IoT (like sensors in agriculture) can focus on supporting many low-data-rate devices with low power consumption. FWA (Fixed Wireless Access) with 5G extends high-speed internet to areas where traditional infrastructure like fiber or cable isn't available, which is crucial for remote or rural IoT applications. This makes it possible to deploy IoT solutions like remote monitoring of agricultural fields. Multi-Access Edge Computing (MEC) brings computation closer to the data source by placing servers and processing power at the network edge, near the IoT devices.
As James and Adam have an exchange on 5G networks, let us understand the uniqueness 5G network communication brings to the table. There are several 5G network capabilities one should know, as 5G adoption is getting popular in the IoT domain. The following are the advancements in 5G networks when compared to its predecessor 4G network.
Fifth Generation (5G)
The fifth generation, or 5G networks, have powered seamless applications around the world, demonstrating that it's not only about the blistering internet speeds but also the seamless experience it uncovers for its users.
5G networks with the wide spectrum of 5G NR mmWave and 5G reduced capability has powered different IoT applications ranging from eMBB (enhanced Mobile Broadband), uRLLC (Ultra-Reliable Low-Latency Communication), and Massive Machine-Type Communication (mMTC).
The Market Research Future states that the 5G Market is projected to grow from 15.03 billion in 2024 to 229.41 billion by 2032, exhibiting a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 40.60% during the forecast period (2024-32).
This market indication is a clear indication that 5G communication is making its mark around all walks of life and all industries including IoT healthcare, Smart BMS and telematics solutions, transport and logistics, smart homes, smart metering, and more.
Millimeter Wave Spectrum
At the heart of 5G's promise of ultra-fast speeds lies the millimeter wave (mmWave) spectrum. Operating at frequencies between 24 GHz and 100 GHz, mmWave opens up vast new highways for data transmission. This high-frequency spectrum, previously untapped for cellular communications, is a game-changer in the world of wireless technology.
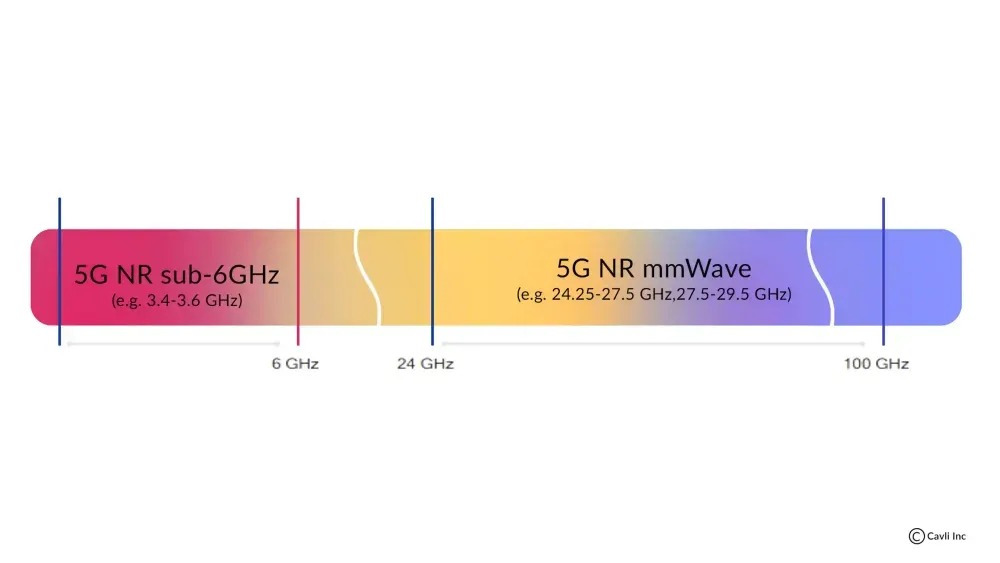
The millimeter wave spectrum refers to the band of radio frequencies between 24 GHz and 100 GHz. This range is characterized by short wavelengths from 1 to 10 millimeters, hence the name "millimeter wave" (mmWave). These frequencies are higher than those traditionally used for mobile communications and can carry large amounts of data at very high speeds, making them ideal for high-bandwidth 5G applications. They are well-suited for densely populated urban areas to provide high-speed internet access over short distances, typically by deploying small cells that cover small geographic areas.
Visit our blog on 5G mmWave and Sub-6 GHz to learn more about the 5G spectrum and its features.
Spectrum Acquisition and Deployment
5G utilizes different radio frequencies (spectrum) compared to 4G. These bands offer faster speeds and lower latency. Each carrier needs its own dedicated spectrum bands. 5G operates on higher frequencies with shorter ranges than 4G. This necessitates installing more cell sites (towers) to ensure wider coverage and consistent performance.
Areas with fewer towers in one carrier's network may experience slower speeds and higher latency compared to areas with denser coverage from another carrier. Also upgrading to high-speed fiber optic cables (connecting cell sites to the core) limits the bottlenecks and congestion, impacting data speeds and overall network performance.
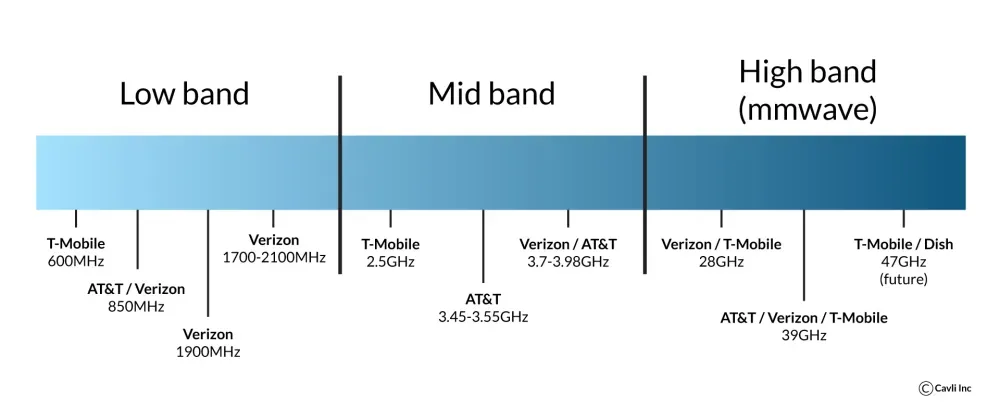
Telecom operators using different bands of Cellular spectrum for their connectivity services
5G Core Network (5GC)
The 5G Core Network (5GC) represents a fundamental shift from the 4G Evolved Packet Core (EPC), both in terms of architecture and functionality. The 5GC is designed to support a wide range of services with diverse performance requirements, from enhanced mobile broadband (eMBB) to ultra-reliable low-latency communication (uRLLC) and massive machine-type communication (mMTC).
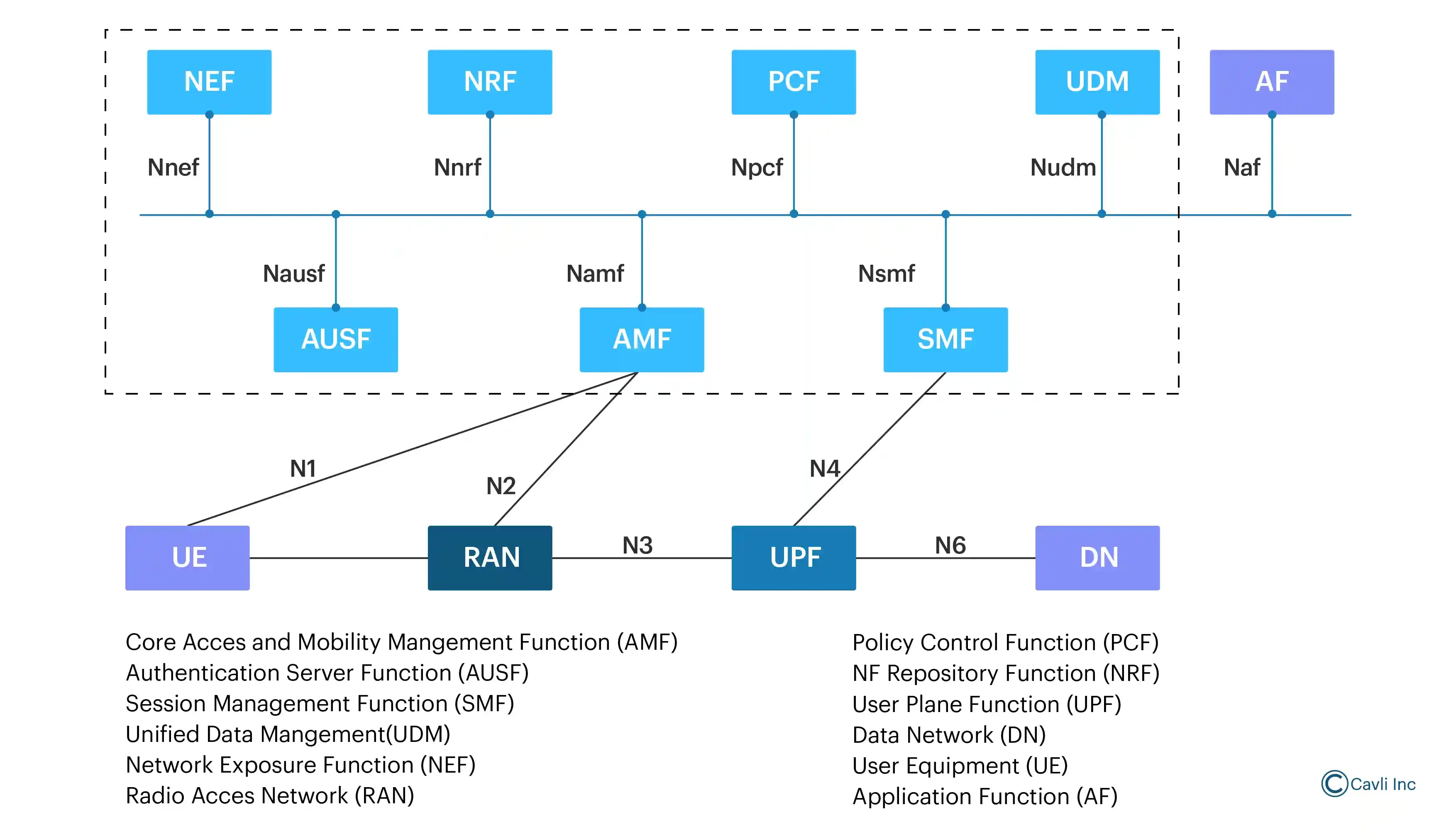
5G Core Network Components
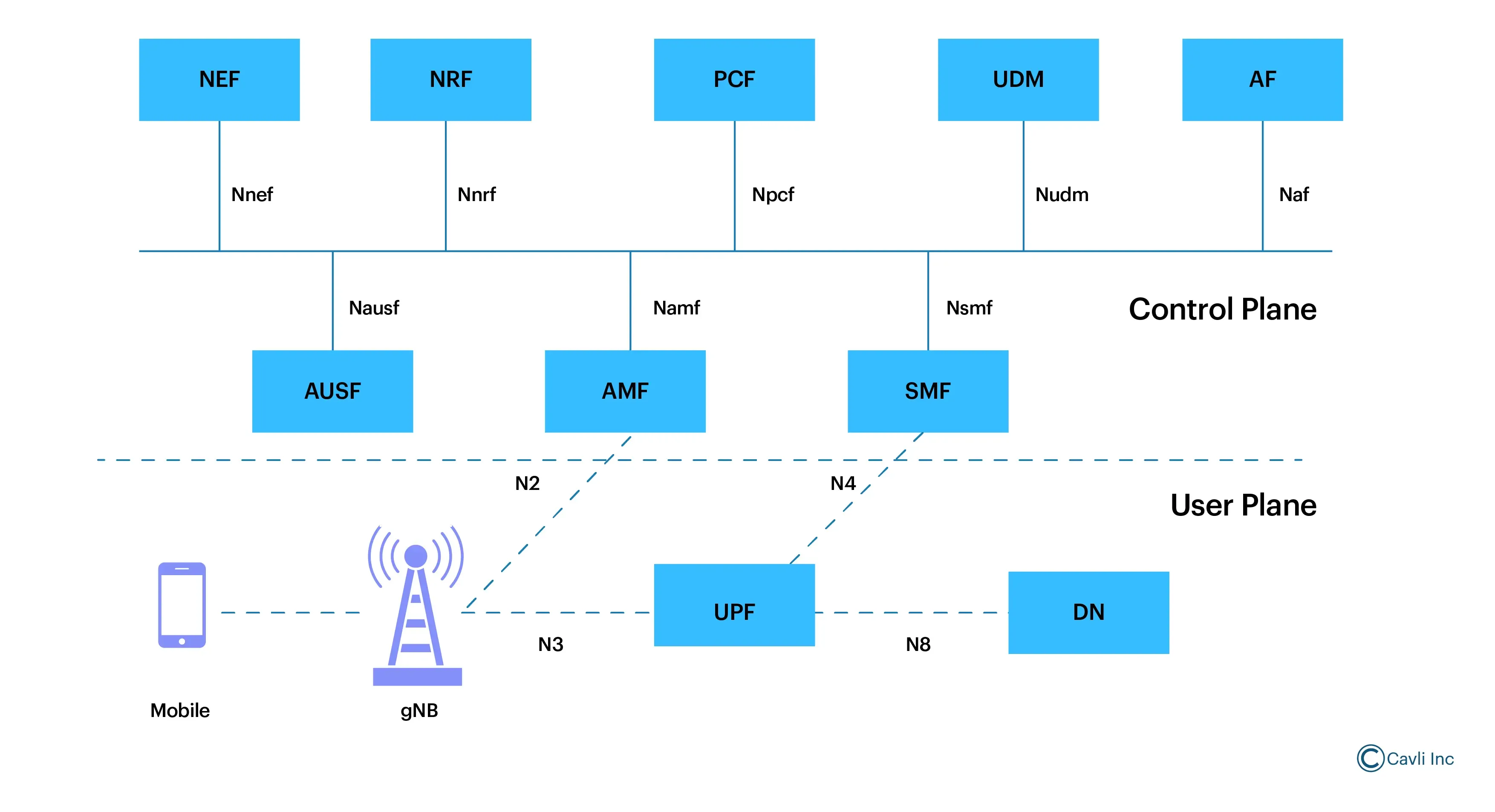
The 5GC is built on a Service-Based Architecture (SBA). In this architecture, network functions are designed as modular, independent services that communicate via standardized APIs over a common, web-based service bus. Each network function (like the Access and Mobility Management Function (AMF), Session Management Function (SMF), and User Plane Function (UPF)) can be deployed, scaled, and upgraded independently, leading to greater flexibility and scalability.
5GC introduces network slicing, which allows the creation of multiple, isolated virtual networks on a shared physical infrastructure. Each slice can be customized for a specific service type (e.g., eMBB, uRLLC, or mMTC), with unique performance, security, and quality of service (QoS) requirements. The 5G Core also introduces a flexible and dynamic QoS model, allowing real-time adjustments based on service requirements and network conditions.
Centralized Radio Access Network
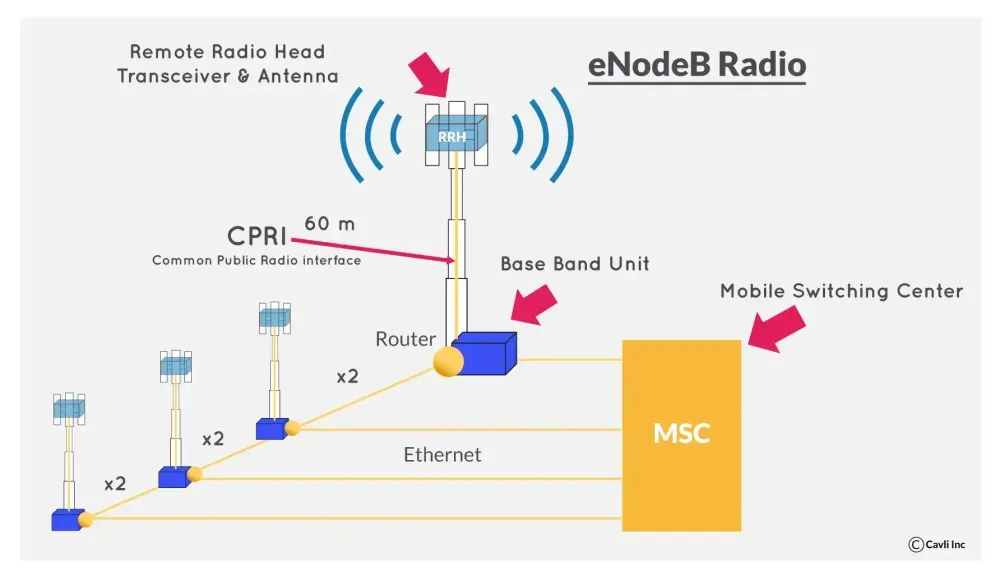
C-RAN structure in 5G networks
C-RAN, which stands for Centralized Radio Access Network, is a key architecture in 5G networks that centralizes baseband processing while distributing radio units closer to users.
Centralized Baseband processing with C-RAN handles complex digital signal processing for data transmission and reception, moving data to a centralized data center instead of being located at each cell site. This enables multiple cell sites to share processing power, optimizing resource utilization and cost-efficiency.
This 5G low latency is game-changing for real-time applications like connected cars to smart homes seamlessly. For improved signal reception and transmission, cell sites are equipped with RRH (remote radio head) handling multiple 5G bands, like sub-6 GHz and millimeter wave (mmWave) frequencies, offering flexibility and adaptability.
Network Slicing
Network slicing is one of the most transformative features of 5G technology, allowing operators to build multiple virtual networks (or "slices") on top of a shared physical infrastructure. Each slice can be tailored to meet the specific needs of different applications or services. Network slicing leverages Software-Defined Networking (SDN), Network Function Virtualization (NFV), and cloud-native principles to create multiple logical networks (slices) that operate on a common physical infrastructure. Each slice can be independently managed and optimized for different types of services or customer requirements. For example:
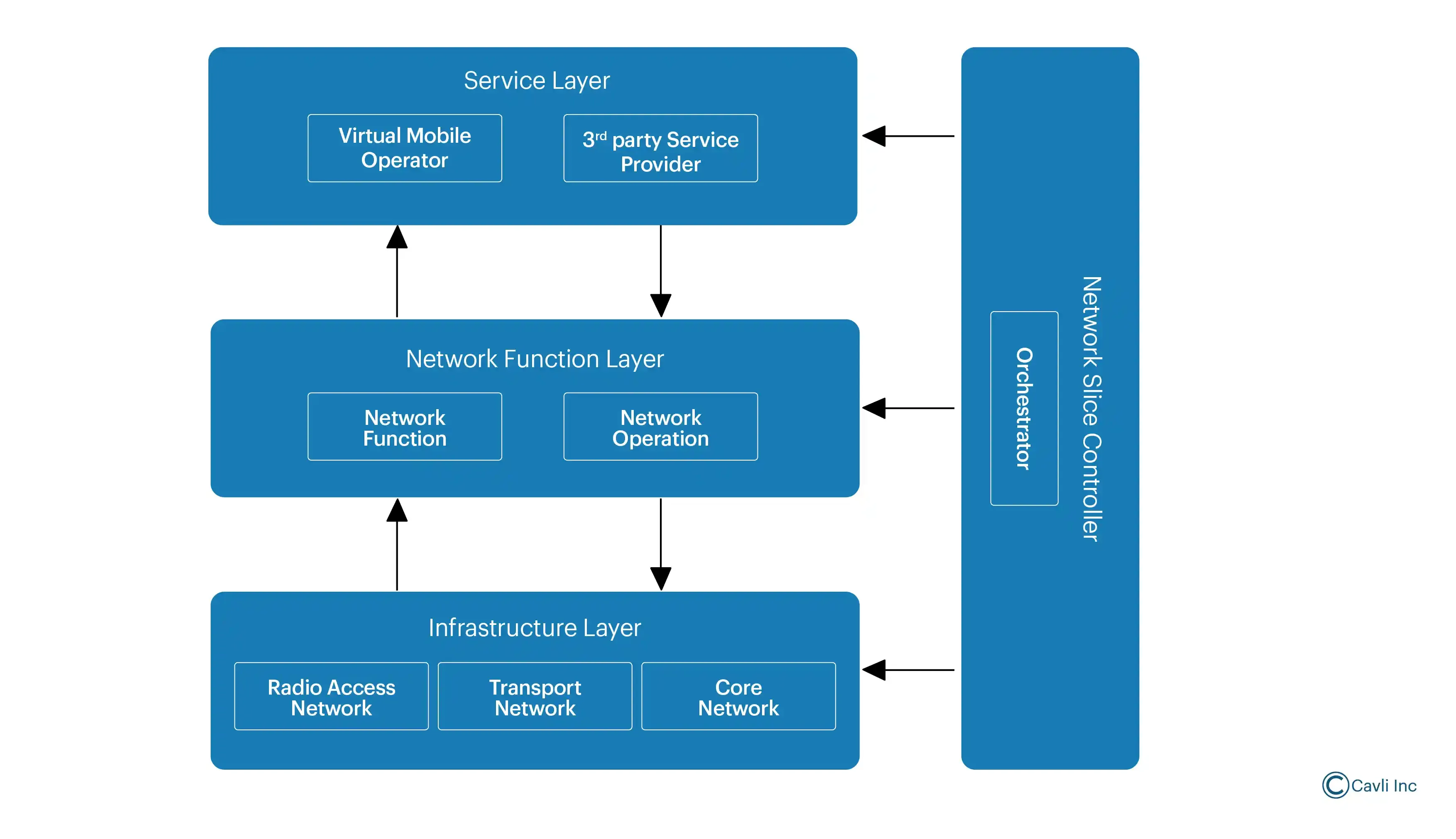
Network Slicing in 5G
- Slice A might be optimized for high-speed video streaming (eMBB) with high data rates and moderate latency.
- Slice B could cater to autonomous vehicles (uRLLC) that require ultra-low latency and high reliability.
- Slice C might be designed for IoT applications (mMTC) with massive connectivity but lower data rates.
Network slicing involves several IoT layers, each responsible for different aspects of slice creation and management:
- Infrastructure Layer: It serves as the foundation upon which virtual network functions (VNFs) are deployed.
- Network Function Layer: This layer consists of VNFs that provide the essential functions required for network operation, such as session management, mobility management, and user data processing.
- Service Layer: This layer interacts with the network function layer to ensure that each slice adheres to its service-level agreement (SLA) by allocating appropriate resources and configuring network paths.
- Management and Orchestration Layer (MANO): The MANO layer manages the lifecycle of network slices, from creation and configuration to monitoring and optimization.
Visit our blog on IoT Architecture in IoT Systems to learn more about IoT layers and its functions.
Software-Defined Networking (SDN) and Virtualization
In traditional networks, the network is a tightly coupled system where hardware and software are intertwined. Changing anything requires physical modifications, making it slow and inflexible.
With SDN and virtualization, network functions become virtualized software packages that can run on any compatible hardware, making them flexible and agile. SDN acts as a central brain to manage and orchestrate virtualized functions.
5G demands diverse services with varying needs. SDN allows for the dynamic allocation of resources and on-demand creation of virtual networks, catering to different applications efficiently. With shared hardware across virtual functions, 5G reduces hardware dependency and allows for easier upgrades and scaling, driving cost optimization.
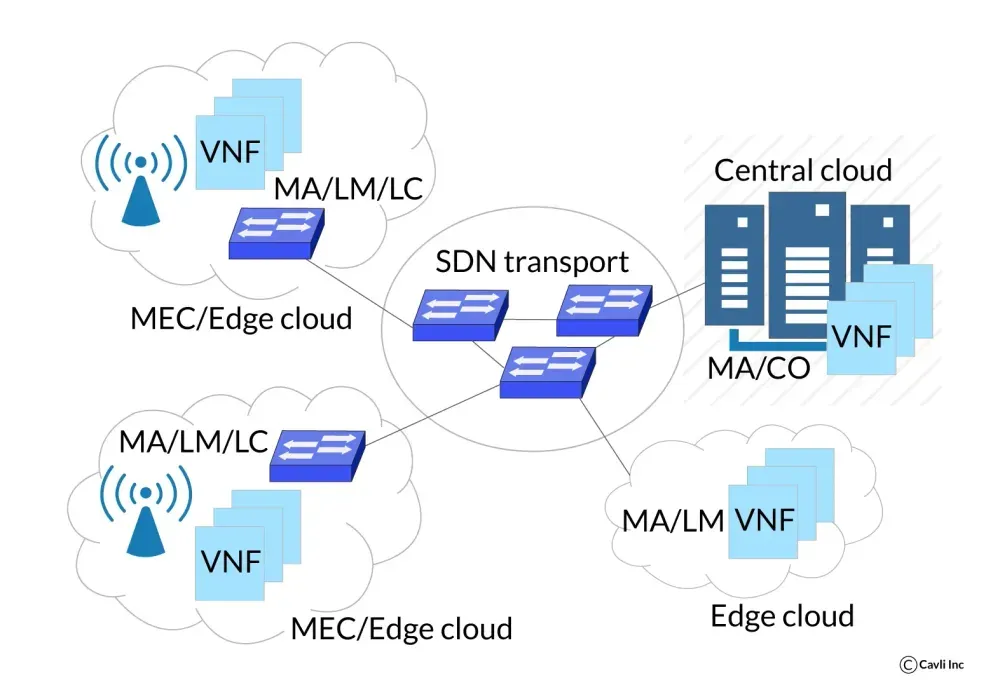
SDN and virtualization in 5G network communication
Control and User Plane Separation (CUPS)
CUPS stands for Control and User Plane Separation, which, as the name suggests, is the architectural approach of separating the control and user planes into distinct functions that can be independently deployed, managed, and scaled.
Control plane and User plane Separation in 5G networks
In a 4G network, the Serving Gateway (SGW) and Packet Data Network Gateway (PGW) handled both control and user plane functions together. This integrated approach made it challenging to scale each function separately based on demand and limited the flexibility in optimizing network performance.
In a 5G network, CUPS fully decouples control and user plane functions, allowing them to be deployed and managed separately. CUPS enables network operators to reduce capital expenditures (CapEx) and operational expenditures (OpEx) by using more cost-effective infrastructure and optimizing resource utilization.
CUPS is designed to improve network flexibility, scalability, and efficiency by separating the control functions (like managing connections and mobility) from the data forwarding functions (like handling user traffic). This separation enables better optimization and distribution of network resources, particularly in the context of 5G, which supports diverse services with varying performance requirements.
Dynamic Spectrum Sharing (DSS)
Dynamic Spectrum Sharing (DSS) is a key technology in 5G networks that allows both 4G LTE and 5G NR (New Radio) to coexist and share the same frequency spectrum dynamically. Dynamic Spectrum Sharing (DSS) is a technique that allows the same frequency band to be used for both 4G LTE and 5G NR transmissions.
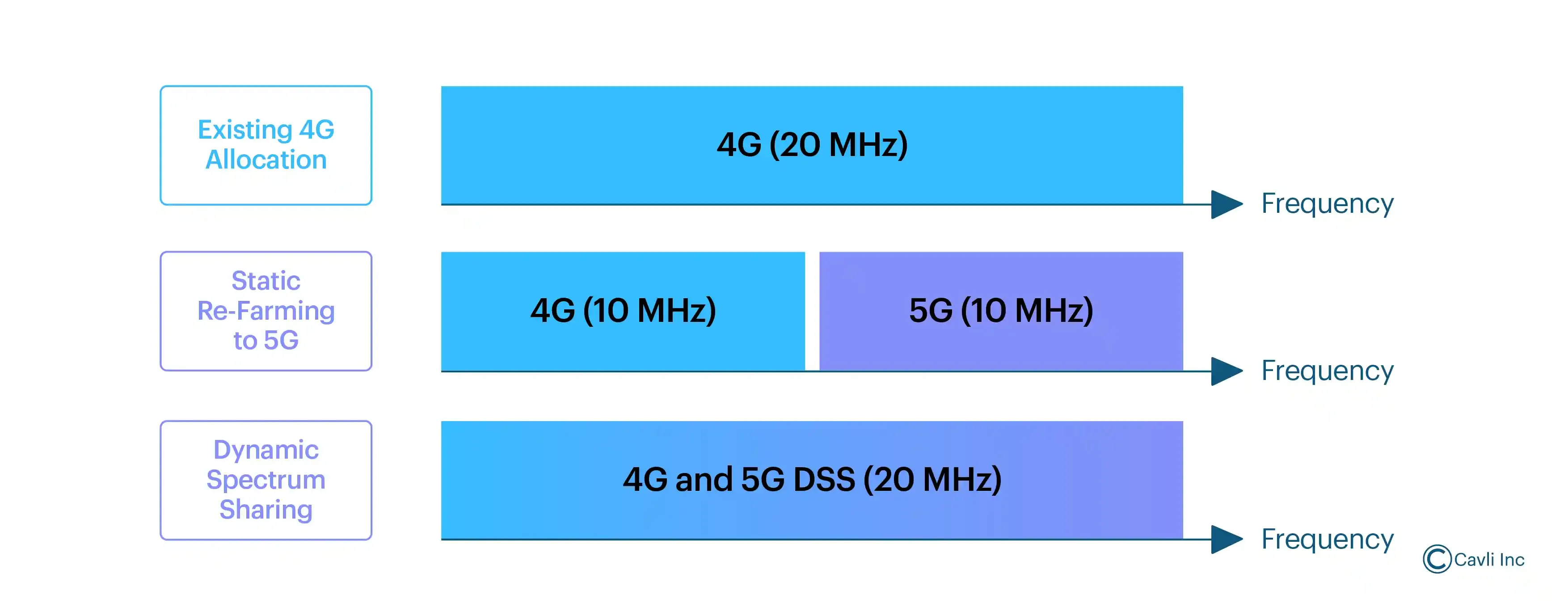
Dynamic Spectrum sharing in 5G networks
Instead of dedicating specific frequency blocks exclusively to one generation of technology (as is traditionally done), DSS dynamically allocates spectrum resources between 4G and 5G users based on real-time demand.
The spectrum resources are divided into time slots or resource blocks. In DSS, the base station dynamically assigns these slots to either 4G LTE or 5G NR traffic. This allocation can change from one slot to the next, allowing the network to adapt to changing demand patterns in real-time.
This is achieved using a scheduling algorithm that considers various factors, such as the type of traffic (e.g., voice vs. video), the priority of services, and the QoS requirements for both 4G and 5G users.
Massive MIMO
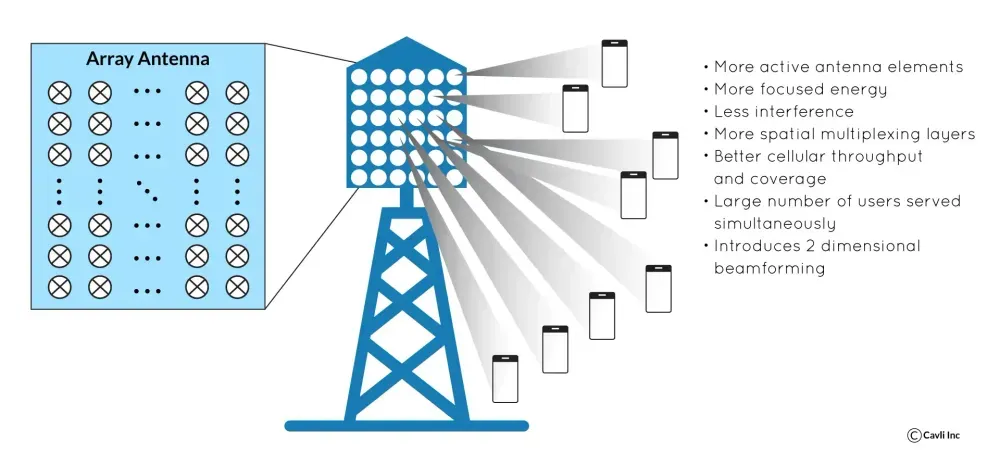
Massive MIMo in 5G technology
MIMO stands for Multiple Input, Multiple Output, and it's a key technology used in both 4G and 5G networks to increase data transmission rates and improve overall network performance. Massive MIMO is crucial for increasing network capacity and focusing signals directly to users. They reduce interference and improve signal strength, especially in crowded environments.
With multiple antennas, MIMO achieves two main benefits, Spatial Multiplexing and Spatial Diversity. 5G networks take MIMO to the next level with Massive MIMO, which utilizes a significantly larger number of antennas (e.g., dozens or even hundreds) compared to traditional MIMO setups. This leads to even greater capacity and performance gains. More simultaneous data streams can be transmitted, enabling ultra-fast speeds for applications like high-definition video streaming and virtual reality. Signal quality is boosted, reaching more users and extending coverage into areas with weak signals. By focusing beams on specific users, MIMO improves spectrum efficiency and allows more users to share the network effectively.
Visit our blog on MIMO technology learn more about Massive MIMO in 5G networks.
Beamforming
In 5G networks, beamforming is a sophisticated technique used to focus radio waves in a specific direction, rather than broadcasting them in all directions like traditional antennas. By aiming the radio waves directly at a specific user's device, beamforming strengthens the signal and reduces interference from other devices or sources of noise. This translates to better signal quality, fewer dropped connections, and faster data speeds. With beamforming, multiple users can receive strong, focused signals simultaneously, even in high-traffic areas. Since beamforming concentrates the radio waves on specific targets, it reduces the need for high-power transmissions. This results in lower energy consumption for both base stations and user devices, improving sustainability and battery life.
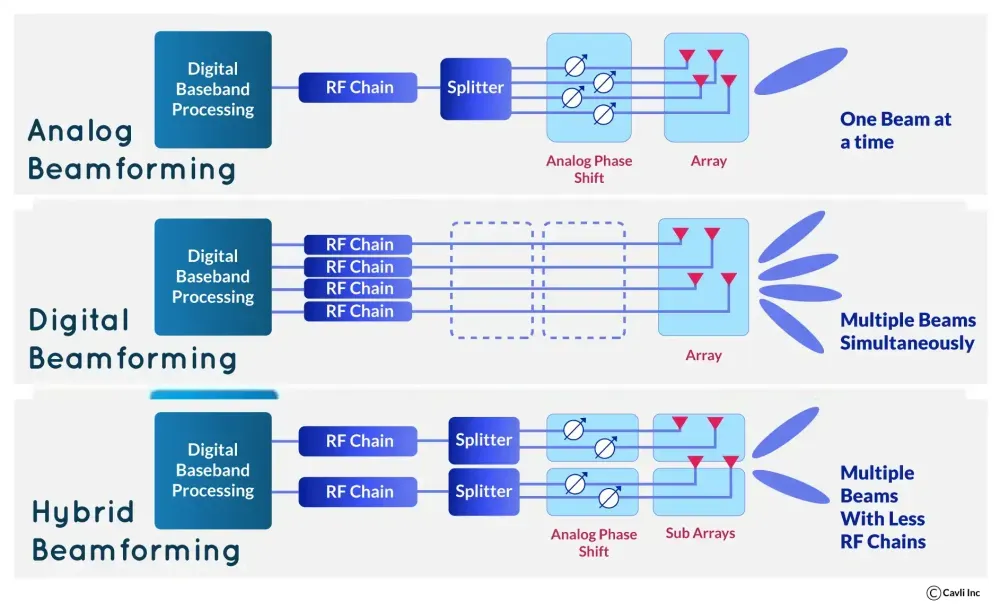
Beamforming technique in 5G communication channels
There are three main types of beamforming used in 5G networks:
Analog Beamforming:
Analog beamforming uses phase shifters in the analog domain to adjust the signal phase emitted by each antenna element. By controlling the phase, signals combine constructively in a specific direction, forming a focused beam toward the desired user equipment (UE). This method is simple and efficient in terms of implementation and power consumption but lacks flexibility.
Digital Beamforming:
Digital beamforming involves processing the signal in the digital domain before analog conversion for transmission. This method allows for complex signal manipulation, enabling the creation of multiple beams with varying characteristics simultaneously. It supports features like multi-user MIMO and spatial multiplexing, enhancing network capacity and efficiency. However, it requires more complex hardware and consumes more power than analog beamforming.
Hybrid Beamforming:
Hybrid beamforming combines both analog and digital beamforming techniques. It performs coarse beamforming in the analog domain using phase shifters, followed by fine adjustments in the digital domain. This approach balances the flexibility of digital beamforming with the cost-effectiveness of analog beamforming, making it suitable for 5G applications such as autonomous vehicles, remote surgery, and industrial automation.
Full Duplex
Full duplex technology allows a device to transmit and receive data simultaneously on the same frequency channel, potentially doubling the speed compared to traditional half-duplex systems, which handle either transmission or reception at a time. 5G networks leverage Full-Duplex Time Division Duplex (TDD) and Full-Duplex Frequency Division Duplex (FDD) to enhance communication efficiency by optimizing time and frequency slots for simultaneous data transfer.
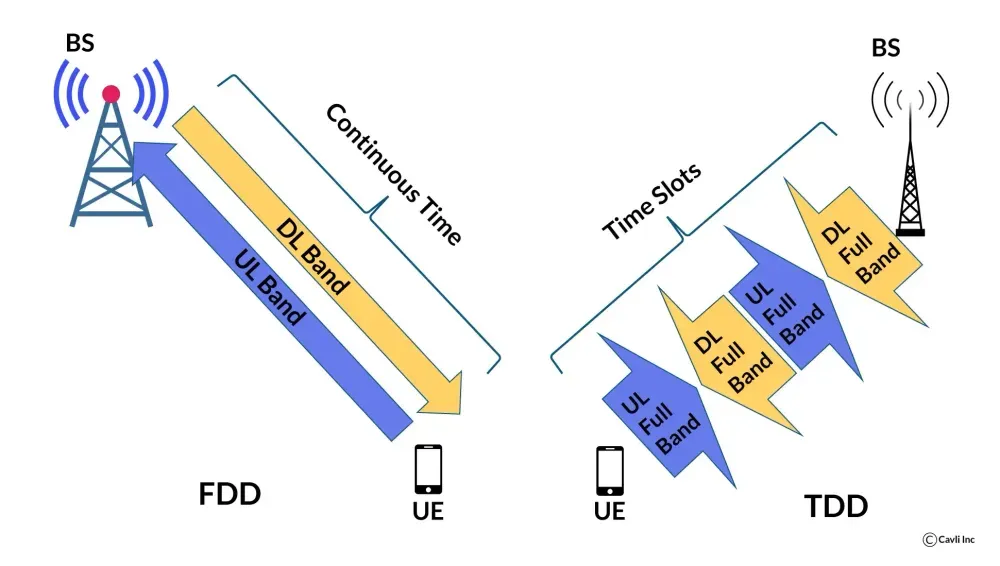
Two- way communication with FDD and TDD in 5G
Both FDD and TDD enable two-way communication in 5G, but they differ in their approach. FDD uses separate frequency bands for uplink and downlink, like two lanes on a highway. It's simpler to implement but requires more spectrum.TDD shares the same frequency band but divides it into time slots for uplink and downlink, like traffic alternating directions on a single lane. It's more spectrum-efficient but requires complex synchronization and can experience interference.
Visit our blog on Cellular Frequency Bands to learn more about TDD and FDD in cellular communications.
Multiband Operation
In 5G networks, Multiband operation refers to the capability of a device (phone, tablet, etc.) or network to utilize multiple frequency bands simultaneously for data transmission and reception. This means the device or network can switch between different bands depending on factors like signal strength, data demand, and network congestion.
There are two main types of Multiband operation in 5G.
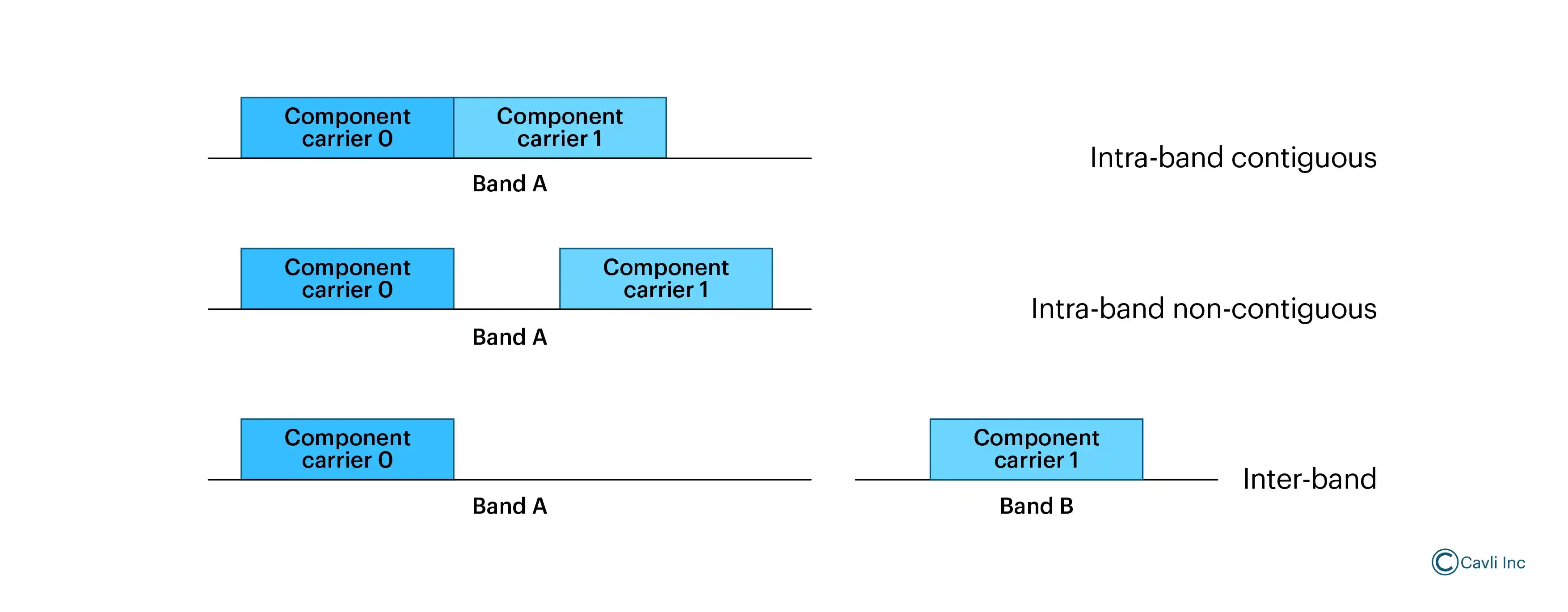
Intra-band Carrier Aggregation
Intra-band CA combines multiple channels within the same frequency band to increase total bandwidth and data speeds.
For example, a device may combine two 20 MHz channels in the C-band (3.3-3.8 GHz) to achieve a peak download speed of 400 Mbps.
Inter-band Carrier Aggregation
Inter-band CA combines channels from different frequency bands, offering wider coverage and leveraging the strengths of each band.
For example, a device might use a high-frequency band like mmWave (26 GHz) for peak speeds in close proximity to a cell site, then seamlessly switch to a lower band like C-band for wider coverage when moving away.
By combining multiple bands, 5G offers higher peak speeds and faster downloads. Utilizing lower bands ensures wider network reach and connectivity even in remote areas. Switching between bands based on network congestion and data demand ensures a smooth and reliable user experience.
Closing Notes:
With 5G there are several advancements including the shift to a cloud-native core, service-based architecture, and enhanced RAN technologies like Massive MIMO, network slicing and others revolutionizing 5G mobile networks. These innovations enable ultra-low latency, high scalability, and unprecedented flexibility, paving the way for diverse applications from IoT to autonomous systems. By fully leveraging these advancements, 5G sets a robust foundation for future technological growth and innovation.
5G RedCap Modules by Cavli Wireless
Discover Cavli Wireless's cutting-edge 5G RedCap modules, built on Qualcomm chipsets with integrated GNSS and eSIM capabilities. These modules support 4G fallback, ensuring seamless connectivity for IoT applications. Easily manage and optimize 5G IoT deployments with Cavli’s Hubble platform, unlocking the full potential of 5G in various industries.
Amusing Tech Chronicles
Facts and Anecdotes Related to this Edition of Wireless By Design
The App Store of Telecommunications
5G networks are like the "App Store" of telecommunications. Unlike 4G, which was built on rigid, hardware-based systems, 5G's cloud-native architecture allows operators to launch new services quickly, much like downloading an app. This flexibility means new features and improvements can be deployed in real-time without significant downtime.
The Lane System
In 2024, NTT DoCoMo in Japan announced the deployment of an end-to-end orchestration (E2EO) 5G standalone network slicing to create dedicated network slices for industrial automation. These help them to prioritize high precision applications. Network slicing allows operators to create "mini-lanes" for specific purposes on the same infrastructure just like on a highway: a fast lane for emergencies, a dedicated lane for public transport, and another lane for others.
The Flexible Workspace
Imagine a flexible office space. Instead of fixed departments, the building has modular areas that can be reconfigured based on the requirement. If the sales team expands for a big project, they can quickly take over more space and as the project ends, the space can be reallocated to other teams in need. This is how Dynamic Spectrum Sharing (DSS) works in 5G. It allows 4G LTE and 5G to share the same frequency spectrum dynamically. When there’s more demand for 5G services, the network can allocate more spectrum to 5G, and vice versa.
Go Beyond and Explore
What is 5G Standalone Architecture?
5G Standalone (SA) Architecture is a deployment model for 5G networks where the 5G New Radio (NR) connects directly to a 5G Core Network (5GC), without relying on any existing 4G LTE infrastructure. The cloud-native 5G core in SA is designed for flexibility, supporting rapid scaling, dynamic resource allocation, and agile service deployment. This flexibility is crucial for supporting diverse use cases, from consumer mobile broadband to industrial automation. SA Architecture enables advanced 5G features such as network slicing, Multi-Access Edge Computing (MEC), Control and User Plane Separation (CUPS), and enhanced Quality of Service (QoS) controls, which are not fully supported in the 5G Non-Standalone (NSA) model.
Explain Service-Based Architecture in 5G?
Service-Based Architecture (SBA) is a fundamental design principle in the 5G Core Network (5GC) that shifts from traditional monolithic and hardware-centric network designs to a more flexible, modular, and cloud-native approach. In SBA, all communication between network functions occurs via standardized RESTful (Representational State Transfer) APIs. This allows for seamless interaction, integration, and interoperability among different network components, regardless of the vendor.
What is 5G Edge Slicing?
5G Edge Slicing involves the implementation of network slicing specifically at the network edge, closer to end users or devices. It entails creating localized network slices that operate nearer to end-users, utilizing edge computing infrastructure, such as Multi-Access Edge Computing (MEC) servers. By processing data locally at the edge of the network rather than sending it back to a centralized data center or cloud server, 5G edge slicing reduces latency and enhances the user experience, particularly for applications requiring real-time feedback.





