Introduction
IoT deployments worldwide have used conventional SIM cards for a long time from the early 2000s, when it was first used in the Automated Meter Reading (AMR) project in Texas. But, as IoT deployments grew, there arose many difficulties in IoT Connectivity enablement and management.
Conventional SIM cards are carrier-specific. Locked into a single carrier, it will require physical SIM swaps to switch between networks, which obviously seems like an impractical thing to do. A single network SIM could lead to significant connectivity blackouts, especially in the below mentioned two scenarios
- IoT-enabled deployments in mobility
- Deployments are in remote locations, where that particular carrier may not have good coverage
Frequent human intervention and associated recurring costs to just maintain ‘Connectivity’ is not a smart proposition, and requires a technology upgrade/innovation to solve this problem. To address these shortcomings, the eUICC concept came into play.
Transitioning From UICC to eUICC
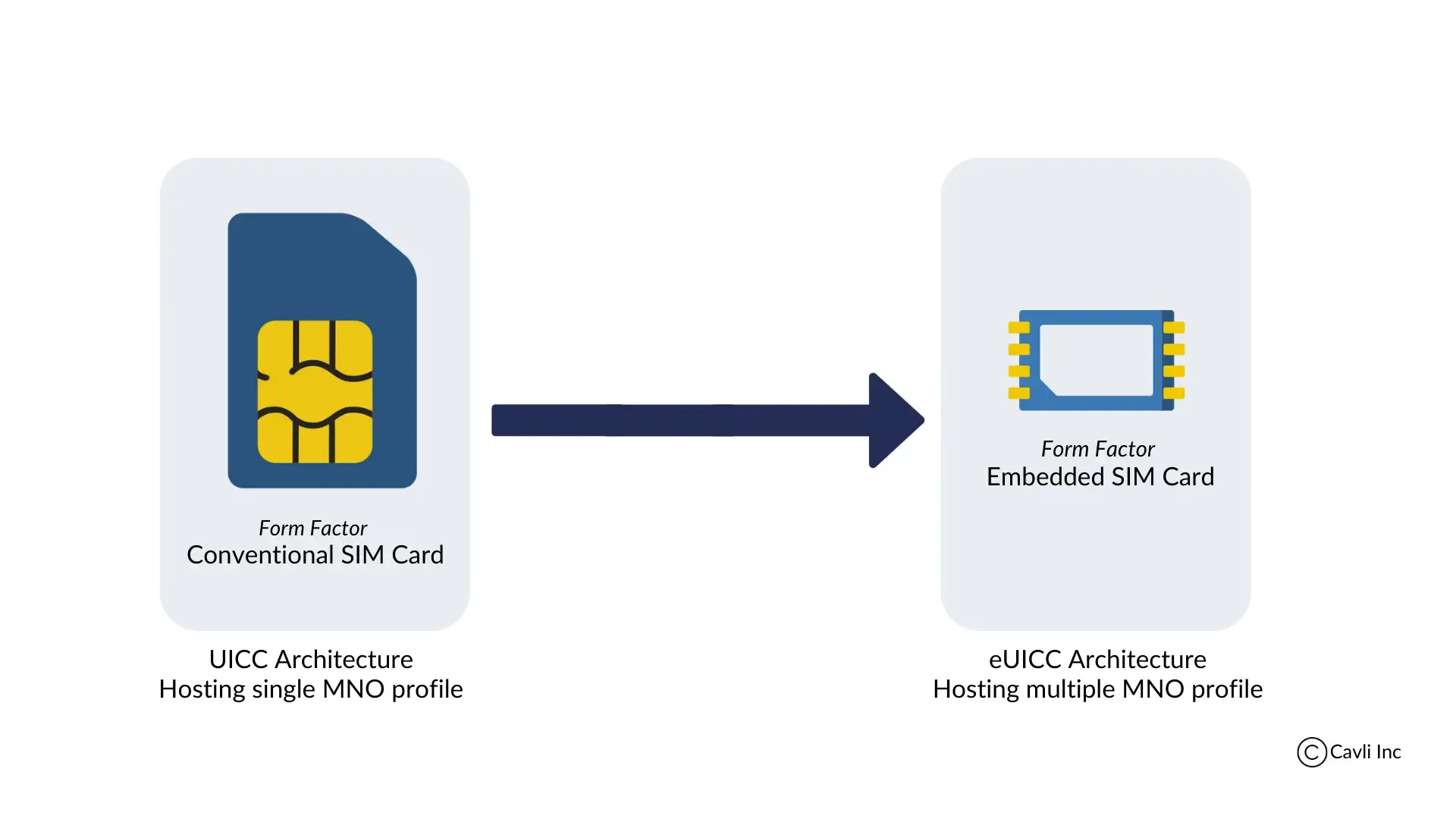
The transition from traditional UICC SIM cards to eUICC-enabled eSIMs
The UICC (Universal Integrated Circuit Card) is known as the mini-computer in the SIM ecosystem. It is a smart card technology that ensures the authentication and identification of SIM cards with designated MNOs.
What is eUICC?
eUICC (Embedded Universal Integrated Circuit Card) is a GSMA-standardized architecture designed to enhance eSIM capabilities for IoT (Internet of Things) and mobile networks. With eUICC, devices can benefit from advanced connectivity features, including Remote SIM Provisioning (RSP) and Over-The-Air (OTA) updates, which make it possible to manage and switch multiple carrier profiles remotely. This technology empowers IoT devices with cross-border connectivity and supports multi-network IoT solutions, significantly reducing the need for physical SIM swaps and manual interventions.
Capabilities of eUICC Technology
Manage Multiple SIM Profiles
eUICC-enabled devices can hold and switch between several SIM profiles, essential for cross-border IoT deployments that require devices to operate in diverse networks across multiple countries. This functionality simplifies SIM management, especially for devices deployed in remote or widely distributed locations.
Load New Carrier Profiles Remotely
With eUICC technology, businesses can remotely load new carrier profiles, invaluable for companies deploying fleets of IoT devices across various regions. eUICC allows organizations to stay competitive by switching to networks that offer better rates, coverage, or regulatory compliance without needing physical interventions. This ensures scalability for applications in asset tracking, logistics, andindustrial IoT.
Effortlessly Switch Between Carriers
By supporting automatic carrier switching, eUICC ensures that IoT devices connect to the most reliable and cost-effective networks available. This feature is critical for industries that require continuous connectivity despite geographic shifts, such as connected vehicles in the automotive sector, patient monitoring devices in healthcare, and public safety sensors in smart cities.
Architecture of eUICC- Explained
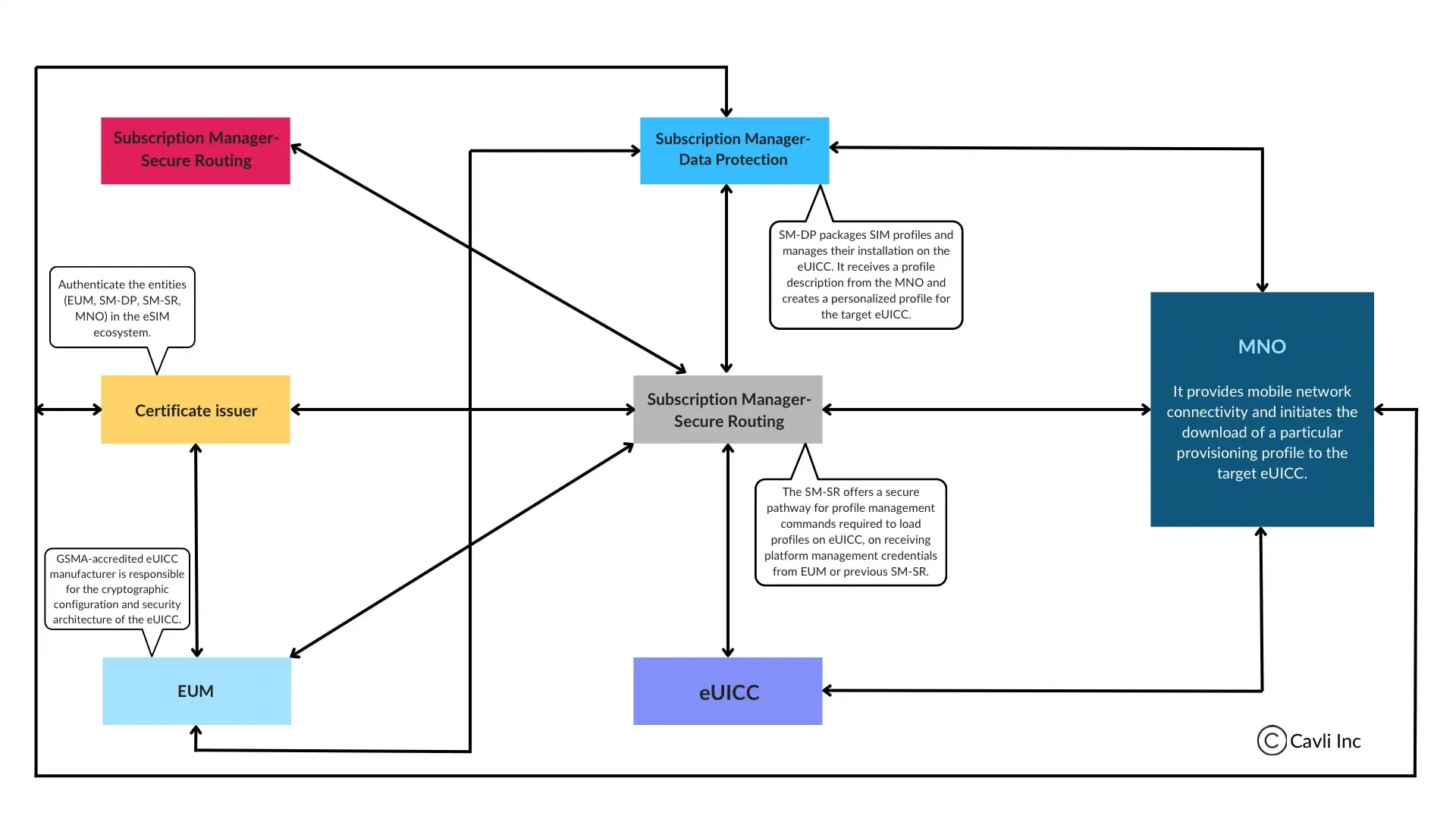
Architectural overview of the eUICC security in eSIM
With tech growth, eUICC capability is now available in removable SIM cards and eSIMs. The key elements constituting the eUICC architecture are:
- SM-DP
- SM-SR
- ISD-R
- ECASD
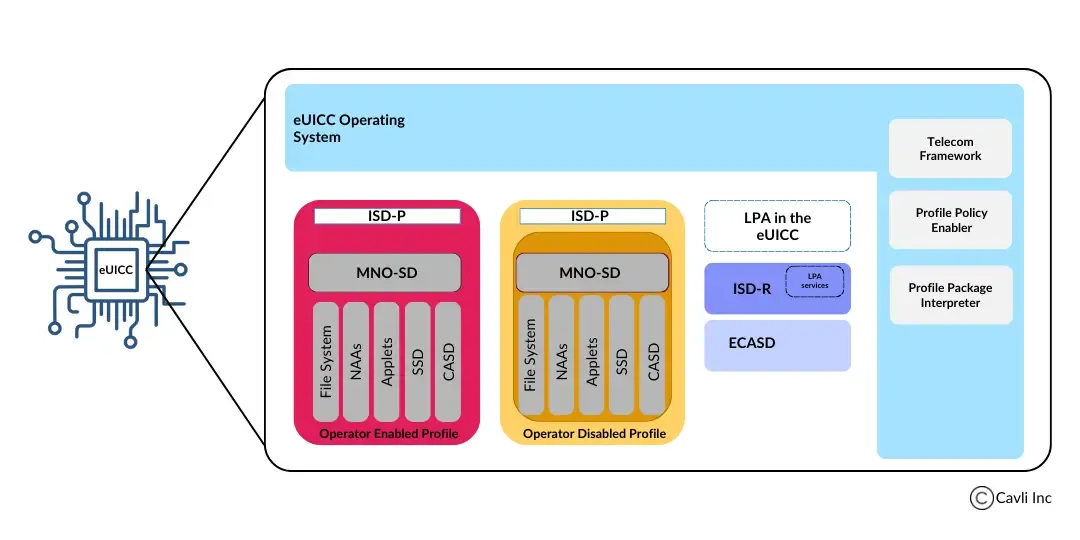
eUICC remote provisioning components of an eSIM
The Subscription Manager (SM) of eUICC has two components:
- SM-DP (SM- Data Preparation)
- SM-SR (SM- Secure Routing)
SM-DP prepares and stores operator profiles, and installs them onto the eUICC. SM-SR manages profile status, enables/disables/or deletes profiles, and secures the link between eUICC and SM-DP during operator profile delivery.
Issuer Security Domain Root (ISD-R) is the in-build card component on SM-SR that manages SIM profiles. The ISD-P represents the UICC profiles. ECASD is also known as eUICC Controlling Authority Security Domain. It contains non-modifiable eUICC private keys, and root public keys for the establishment of new keysets in the ISD-P(s) and ISD-R. The Local Profile Assistant (LPA) component handles profile discovery, downloading profiles, and profile management.
Benefits of eUICC-Enabled eSIMs
eUICC SIM cards enable remote SIM provisioning
The remote provisioning of mobile network operator profiles helps switch between the network carrier profiles. This ensures flexibility and optimum coverage for IoT solutions deployed globally.
eUICC eSIMs offer remote device management with OTA updates
It is now easier for IoT engineers and manufacturers to connect and upgrade their IoT solutions deployed across the globe.
eSIM with eUICC capability enables localization
With OTA and RSP capability, eUICC SIM stores and manages updates of local network carrier profiles in which IoT solutions are deployed. Thus, it mitigates coverage and roaming difficulties making it cost-efficient for IoT solution providers.
Real-World Applications of eUICC in IoT
eUICC technology is transforming multiple industries by providing scalability, flexibility, and cost efficiency for IoT solutions. Here’s how it’s making an impact:
Automotive Industry: Streamlining Global Fleet Management
In the automotive sector, eUICC enables connected vehicles to maintain cross-border IoT connectivity without requiring SIM swaps. For example, a fleet equipped with eUICC-enabled IoT devices can achieve:
- Real-time vehicle diagnostics for proactive maintenance
- Geolocation tracking for fleet optimization
- Over-the-air (OTA) updates to keep software current
This global connectivity improves fleet efficiency, allowing consistent network access and reducing maintenance costs by avoiding physical SIM replacements.
Healthcare: Enabling Continuous, Remote Patient Monitoring
eUICC technology plays a crucial role in healthcare, especially in patient monitoring and medical devices where uninterrupted data transmission is critical. Key benefits include:
- Remote SIM provisioning for real-time monitoring, even across regions
- Support for vital signs tracking and emergency alerts for patients in rural or remote areas
This technology ensures that healthcare devices stay connected, enhancing patient safety and reducing connectivity disruptions during critical situations.
Smart Cities: Powering Infrastructure and Public Safety
Smart cities rely on extensive IoT networks for public safety, traffic, and environmental monitoring. eUICC provides:
- Dynamic network switching to the most reliable and cost-effective carriers
- Support for pollution monitoring, public safety alerts, and traffic flow optimization
eUICC allows for seamless scaling of IoT networks in urban settings, supporting large-scale deployments like sensor arrays and smart meters by enabling automatic, cost-effective network management.
Comparative Advantages of eUICC Over Traditional SIMs
When it comes to IoT connectivity solutions, eUICC offers substantial advantages over traditional SIMs, particularly in large-scale and global deployments. Traditional SIM cards, which require a manual SIM swap to change networks, are often cost-prohibitive and impractical for IoT applications where devices are spread across vast geographic areas or difficult-to-access locations. With eUICC, IoT devices can remotely switch between network providers without physical intervention, ensuring consistent connectivity even in remote or changing environments. This is crucial for industries like logistics and asset tracking, where uninterrupted connectivity is vital to real-time updates and operational continuity.
Traditional SIMs also require individual carrier agreements, which can be costly, especially for multinational deployments where high roaming fees and complex regulatory requirements often arise. With eUICC, businesses can employ a multi-network IoT solutions strategy, allowing devices to store multiple profiles and choose the most effective and affordable carrier based on the device’s current location. This approach significantly reduces costs, minimizes downtime, and ensures reliable global connectivity, especially in mission-critical sectors.
Addressing Misconceptions and Overcoming Key Challenges with eUICC
Despite eUICC’s clear advantages, several misconceptions and challenges may deter companies from fully leveraging this technology. A common myth is that eUICC’s setup is complex and suitable only for large enterprises. However, recent advancements in remote provisioning platforms have simplified the process, making it accessible for businesses of all sizes to achieve scalable IoT connectivity.
Additionally, there are concerns about network compatibility and the false belief that eUICC works only with specific carriers. In reality, as eUICC adoption grows, telecom providers worldwide are enhancing their networks to support this technology, making cross-border IoT connectivity with eUICC increasingly seamless. Compatibility with older network infrastructure and certain regional regulations may pose challenges, but these are being mitigated as providers align with international eUICC standards.
Closing Notes
As the technology makes progress, there is more evolution occurring in this SIM field. The introduction of iUICC with iSIM invention is a topic in itself to discuss later on in the coming chapters. With xUICC ( eUICC & iUICC), it is evident that the connectivity issues in the M2M domain will be addressed to a great extent.
To learn more, visit us at https://www.cavliwireless.com/iot-modules/cellular-modules
Amusing Tech Chronicles
Facts and Anecdotes Related to this Edition of Wireless By Design

A Global Citizen Passport
eUICC is the passport of IoT devices. They allow devices to 'travel' internationally without the hassle of 'visa applications' (carrier negotiations and contracts) for each country.

Go Green
eUICC is environment-friendly. Fewer physical SIM cards mean less plastic waste, making a small but yet a significant green solution.
The Stamp Collector
eUICC is a stamp collector gathering stamps from different (carrier) countries in the world of connectivity.
Go Beyond and Explore
Is eSIM and eUICC the same?
An eSIM, or Embedded SIM, also known as MFF2 SIM card, is a SIM card that is embedded into the devices to provide a permanent network connection. eSIM is the combination of eSIM hardware, RSP platform, and eUICC architecture. eUICC is an architectural component that adheres to GSMA's specifications enabling remote SIM provisioning, OTA updates, and multiple carrier profile storage, without any physical SIM swap.
What are the primary differences between Consumer eSIM and M2M eSIM?
Consumer eSIM is typically used in mobile phones, tablets, laptops, and other consumer devices with user interfaces, where the user actively downloads the profile, often via a QR code. M2M eSIM, on the other hand, is designed for IoT sensors, utility meters, trackers, and devices that operate with minimal onsite human interaction, where the profile is remotely pushed to the device.
Does eSIM drain the battery life of your IoT deployments?
eSIMs are more power-efficient than traditional SIM cards, meaning they use less power and don't drain your battery as quickly when connecting to the wireless network. The factors that influence battery life in devices with eSIM include switching between networks, high data usage, and overall efficiency of the device.
What is the difference between eUICC and eSIM?
eUICC and eSIM, while related, play different roles. eUICC is the software that enables remote
provisioning and multi-network solutions by allowing IoT devices to manage multiple carrier profiles remotely.
How does eUICC benefit cross-border IoT deployments?
With eUICC, IoT devices deployed internationally can seamlessly switch to local networks, avoiding high roaming fees and providing reliable cross-border IoT connectivity with eUICC. For instance, in applications like international logistics, asset tracking,and connected agriculture, eUICC enables seamless connectivity across multiple regions, enhancing operational efficiency and connectivity uptime.
What security measures are in place for eUICC?
Security in eUICC technology is ensured through encrypted remote provisioning and management platforms. Each SIM profile managed by eUICC is securely encrypted and can be updated or replaced remotely, adhering to stringent security protocols. This security framework allows businesses to deploy IoT devices globally with confidence, knowing that their data and connections are protected, even when switching networks.


